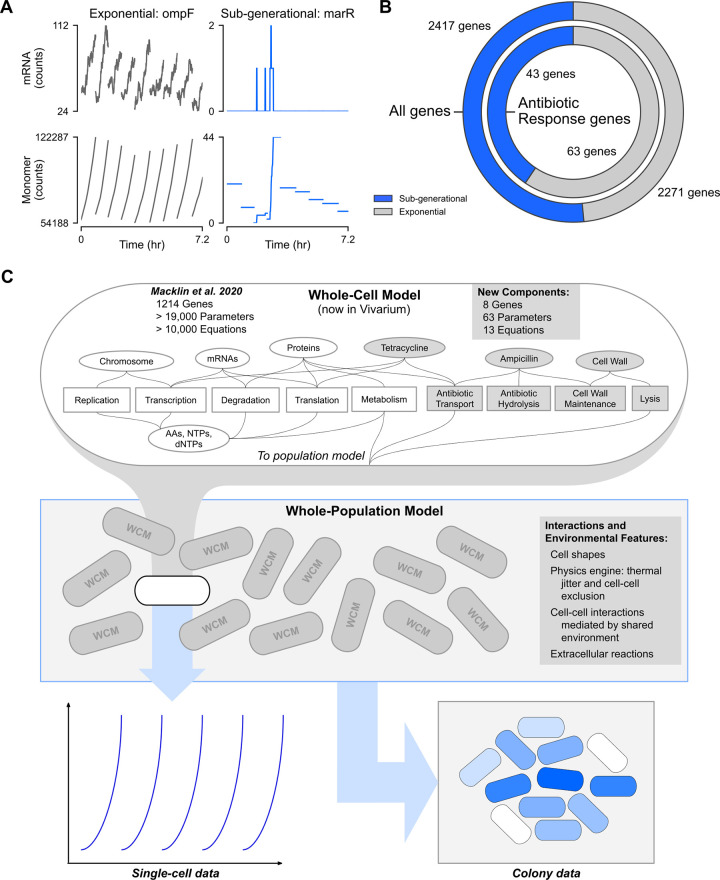
Fig 1. Sub-generational gene expression of antibiotic response genes calls for a multi-scale model of the population-level antibiotic response.
(A) mRNA counts placed above corresponding monomer counts for a gene representative of "exponential" expression (left, ompF) and a gene representative of “sub-generational” expression on the right (right, marR). Data was taken from a representative lineage (cell 011001001 and its ancestors) in the simulated colony (seed 0) grown on minimal M9 medium supplemented with 1 mM glucose. (B) Proportion of all genes (outer ring) and antibiotic response genes (inner ring) that are predicted to be sub-generationally (blue) or exponentially (gray) expressed. Genes were considered sub-generationally expressed if <1 expression event per generation occurred on average in a baseline glucose simulation (seed 10000). (C) Schematic of the expanded E. coli model which can simulate both antibiotic responses and colony growth. The original whole-cell model [22] was supplemented with new functions for 8 genes, 63 new parameters, and 13 new equations. The expanded whole-cell model was then placed inside a spatial environment which supported propagation into colonies composed of many whole-cell model instances that share resources and physically interact. These whole-population models yielded rich time series data for single cells and spatial data for whole colonies.