Figure 1.
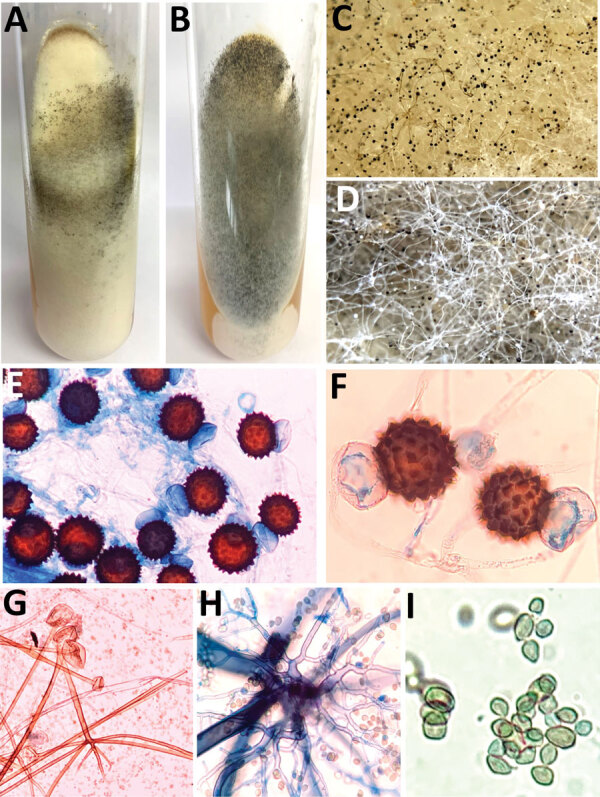
Macroscopic and microscopic characteristics of Rhizopus arrhizus and R. homothallicus isolated from tissue samples from patients enrolled in a 10-month retrospective study, Chandigarh, India, January–October 2021. A, B) Macroscopic appearance of colonies of R. homothallicus (A) and R. arrhizus (B) fungi. C, D) Macro lens image of the colonies showing dark-brown specks in R. homothallicus (C) and black and white dots (salt and pepper appearance) in R. arrhizus (D). E) Photomicrograph from a lactophenol cotton blue mount of R. homothallicus showing multiple reddish brown ornamented zygospores (original magnification ×400). F) Magnified image of E showing unequal suspenser cells and zygospore with prominent spinous projections. G) R. arrhizus showing long, unbranched sporangiophore with nodal rhizoids (original magnification ×200). H) Magnified image of extensively branched rhizoid seen in R. arrhizus. I) Magnified image of sporangiospores of R. arrhizus.
