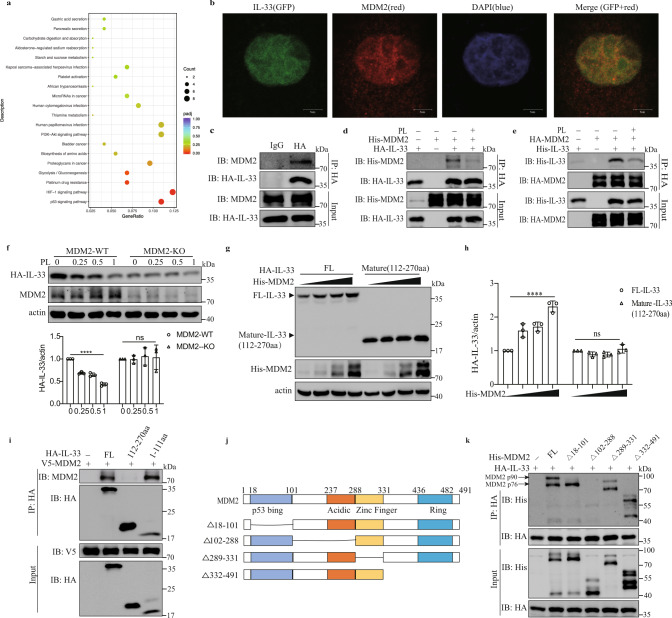
Fig. 6.
MDM2 interacts with IL-33 to facilitate IL-33 stability. a RNA-seq analysis of A549-IL-33 cells treated with or without 0.5 mM PL for 24 h. KEGG pathway analysis showed enriched signaling pathways. b A confocal assay was performed in A549 cells stably expressing full-length IL-33 with GFP. DAPI (blue) and an anti-MDM2 antibody (red) were used (scale bar = 5 μm). c Coimmunoprecipitation of endogenous MDM2 and IL-33 in A549-IL-33 cells. d, e HEK293FT cells were transfected with the indicated plasmids for 24 h and then treated with or without 0.5 mM PL for 24 h before being subjected to immunoprecipitation with an HA antibody. f A549-IL-33 or MDM2-knockout A549-IL-33 cells treated with different concentrations of PL for 24 h. Western blot analysis of intracellular IL-33 levels. The HA-IL-33/actin ratio is shown (n = 3). Ordinary one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test was used to analyze the data. ****p < 0.0001; ns not significant. g, h HEK293FT cells were transfected with full-length HA-IL-33 or mature IL-33 (112–270 aa) and increasing concentrations of His-MDM2. g Western blot showing IL-33 and MDM2 expression. h Ratio of HA-IL-33 to actin expression (n = 3). Ordinary one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test was used to analyze the data. ****p < 0.0001; ns not significant. i Coimmunoprecipitation of HEK293FT cells transfected with IL-33 deletion mutants and V5-MDM2. j Schematic representation of MDM2 and its truncation mutant. k Immunoprecipitation and western blot analysis of HEK293FT cells transfected with HA-IL-33 and truncated MDM2. The data in b–i and k are representative of three independent experiments