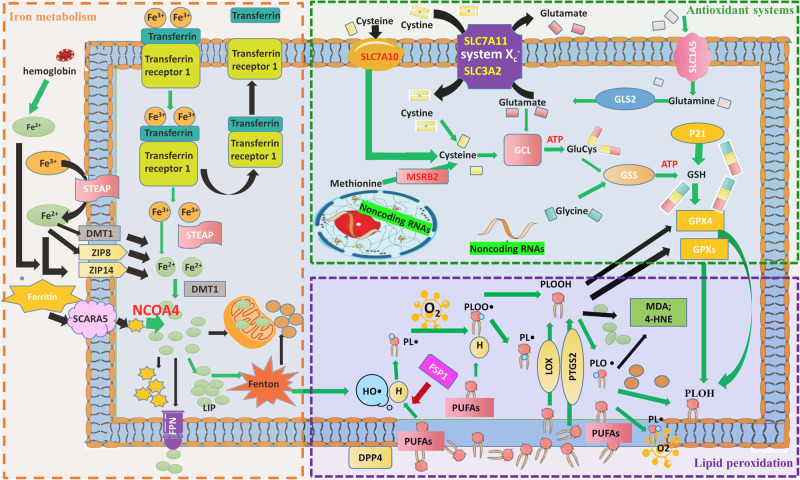
Fig. 1. The process of ferroptosis and the involvement of iron, lipid, and GSH metabolism.
Intracellular excess Fe2+ enters the labile iron pool, causing the Fenton reaction, in which Fe2+ is oxidized to Fe3+, while the electron is transferred to H2O2 to form HO•. HO• initiates the oxidation of PUFAs of membrane PLs. The PUFA of a PL donates a hydrogen atom to HO•, leading to formation of a carbon-centered PL• that further reacts with intracellular molecular O2 to form a PL peroxyl radical (PLOO•). Next, from another PUFA moiety of a PL, PLOO• abstracts a hydrogen atom and is subsequently converted to PL hydroperoxide (PLOOH) accompanied by formation of a new PL•. PLOOH is cleaved in the presence of Fe2+ to form the PL alkoxyl radical (PLO•), which reacts with the PUFA of another PL to form PL alcohol (PLOH) and a new PL•, followed by another lipid radical chain reaction. There are three types of lipid oxidation enzymes: cyclooxygenase (COX), cytochrome P450 (CYP), and lipoxygenase (LOX). They initiate the enzymatic lipid peroxidation process. Lipid peroxides including PL free radicals can be eliminated by GPXs, MDA, or 4-HNE, but excess PL free radicals cause the unbounded peroxidation of PUFAs of membrane PLs, which eventually leads to destruction of the cell membrane. Intracellular Fe2+ and GPX4 are generated via iron and GSH metabolism, respectively. The red arrow represents the inhibitory effect, and the green arrow represents the promoting effect. 4-HNE 4-hydroxynonenal, DMT1 divalent metal transporter 1, DPP4 dipeptidyl peptidase-4, FPN ferroportin (also known as SLC40A1), GCL glutamate-cysteine ligase, GLS2 glutaminase 2, GPX4 glutathione peroxidase 4, GSH glutathione, GSS glutathione synthetase, HO• hydroxyl radical, LIP labile iron pool, LOX lipoxygenase, MDA malondialdehyde, MSRB2 methionine-R-sulfide reductase B2, NRF2 nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2, p21 cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1A, i.e., CDKN1A, PL phospholipid, PL• PL radical species, PLO• PL alkoxyl radical, PLOH PL alcohol, PLOO• PL peroxyl radical, PLOOH, PL hydroperoxide, PTGS2 (encodes cyclooxygenase-2, which is an enzyme that acts both as a peroxidase and a dioxygenase, and catalyzes lipid oxidation), PUFA polyunsaturated fatty acids, SCARA5 scavenger receptor class A member 5, SLC1A5 solute carrier family member 1 member A5, SLC7A11 solute carrier family 7 member A11, STEAP six transmembrane epithelial antigen of prostate, TFR1 transferrin receptor 1, ZIP8 Zrt- and Irt-like protein 8.