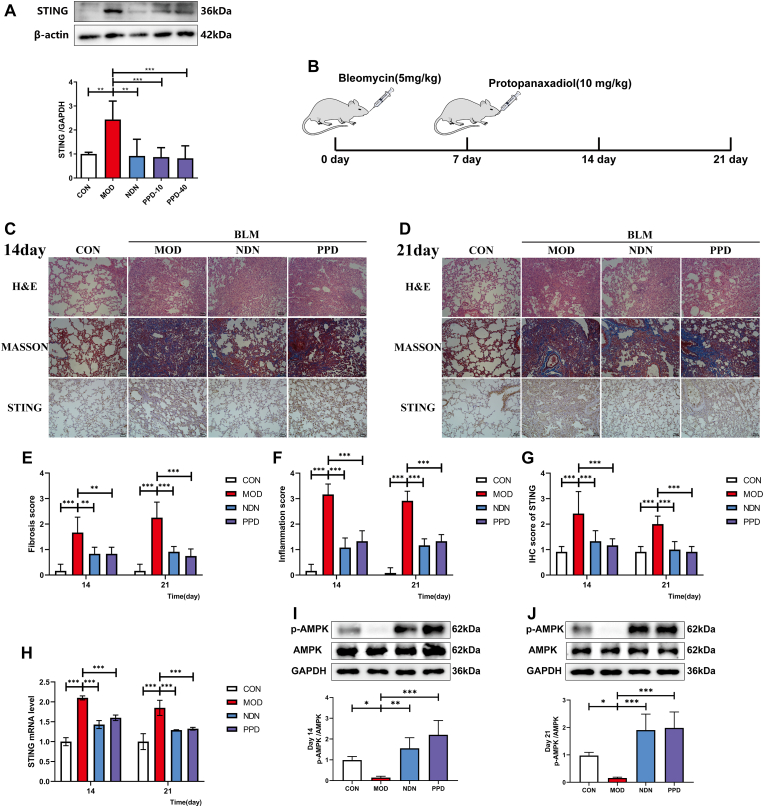
Fig. 3.
Regulation of STING by PPD during bleomycin-induced lung fibrogenesis in mice. (A) Lung STING expression by Western blotting. (B) Scheme showing regulation of STING levels by PPD from BLM-induced mice. Mice were sacrificed for lung tissue sampling on days 14 and 21 after intratracheal administration with 3.5 mg/kg BLM. Intragastric PPD (40 mg/kg) or NDN (40 mg/kg, positive drug) was given for 14 consecutive days after 7 days of intratracheal BLM administration. (C-D) Representative micrographs of H&E, Masson's staining and STING immunohistochemistry in lung pathological sections at days 14 and 21 after intratracheal BLM administration, scale bar = 50 μm. (E&F) Lung inflammation and fibrosis scores at days 14 and 21 after intratracheal BLM administration. (G) Lung immunohistochemical scores; (H) STING mRNA in lung tissue at days 14 and 21 after intratracheal BLM administration by qRT-PCR. (I&J) AMPK and p-AMPK expression in lung at days 14 and 21 after intratracheal BLM administration by Western blotting. Data are expressed as mean ± S.D. (n = 4). ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001.