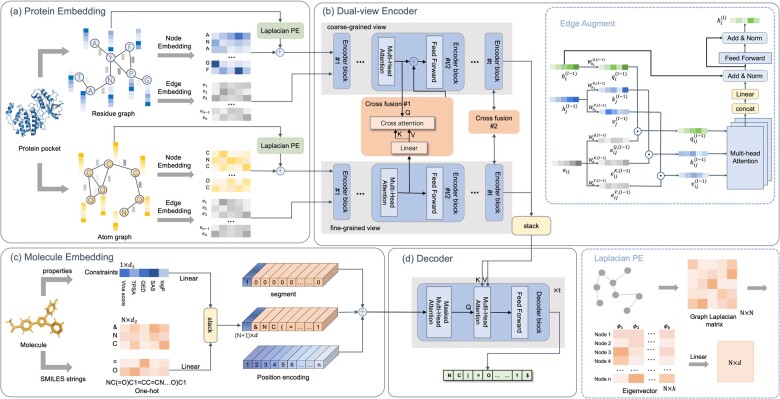
Figure 1.
The framework of CProMG. This framework is composed of four modules, a 3D protein graph embedding module, a dual-view protein encoder, a drug-like molecule embedding module, and a novel molecule decoder. (a) Protein embedding module. A protein (pocket) is represented in a residue graph and an atom graph in parallel. Nodes and edges in each protein graph are embedded. Especially, nodes have additional Laplacian positional encodings. Node representations are also augmented by edge representations. (b) Dual-view protein encoder. It contains two parallel encoder modules w.r.t. protein graph, of which each module is composed of t encoding blocks. Each block contains a multi-head self-attention unit and a feedforward neural network. There are also two cross-attention units between the parallel encoder modules. The concatenation of representations of two encoder modules is output as the protein representation and input into the molecule decoder as the key and value. (c) Molecule embedding module. It encodes physicochemical properties of small molecules, docking scores w.r.t. proteins, and their SMILES sequences simultaneously. The concatenation of them is added with an extra positional encoding as the Query input into the decoder. (d) Molecule decoder. It contains t decoder blocks, each of which contains a masked multi-head attention unit, a cross-attention unit, and a feed-forward network. The decoder autoregressively predicts the next token of the molecular sequence through the generated molecular intermediates and proteins representation.