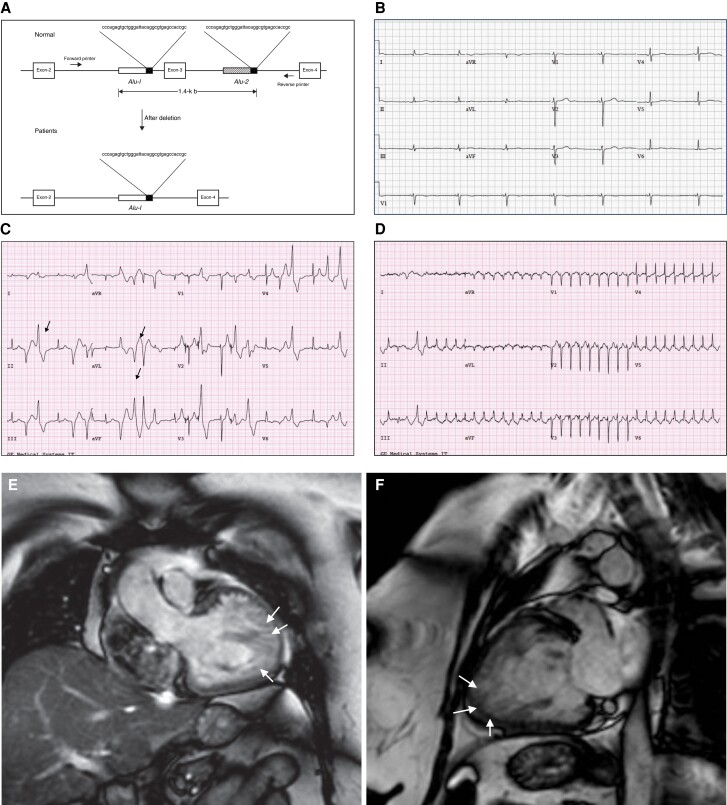
Figure 4.
Exon 3 deletion syndrome clinical phenotype. (A) Alu repeat–mediated RYR2 exon 3 deletion. The diagram represents the Alu-Alu recombination. Alu sequences are located in intron 2, 190 bp upstream from exon 3 and also 536 bp downstream in intron 3. Adapted with permission from Bhuiyan et al.71 (B) 34-year-old female patient with E3DS. Resting ECG showing marked junctional bradycardia at 42 b.p.m. The patient had symptomatic sinus node disease with chronotropic insufficiency. (C) 48-year-old female patient with E3DS. Exercise treadmill testing showed inducible polymorphic ventricular ectopy with intermittent bidirectional ventricular PVCs (arrows). (D) Same patient as (C). Induction of supraventricular tachycardia at peak exercise. The echocardiogram showed a normal sized left ventricular with preserved ejection fraction. However, there was evidence of marked apical and apico-lateral trabeculation meeting criteria for LVNC. (E) and (F) Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging of a 52-year-old female patient with E3DS. The patient developed dilated cardiomyopathy with LVNC and marked systolic dysfunction requiring the insertion of a cardiac resynchronization therapy defibrillator. Note the marked left ventricular apical and apico-lateral hypertrabeculations (arrows).