Fig. 3. Mef2d inhibits the early Tfh differentiation of antigen-specific CD4 T cells.
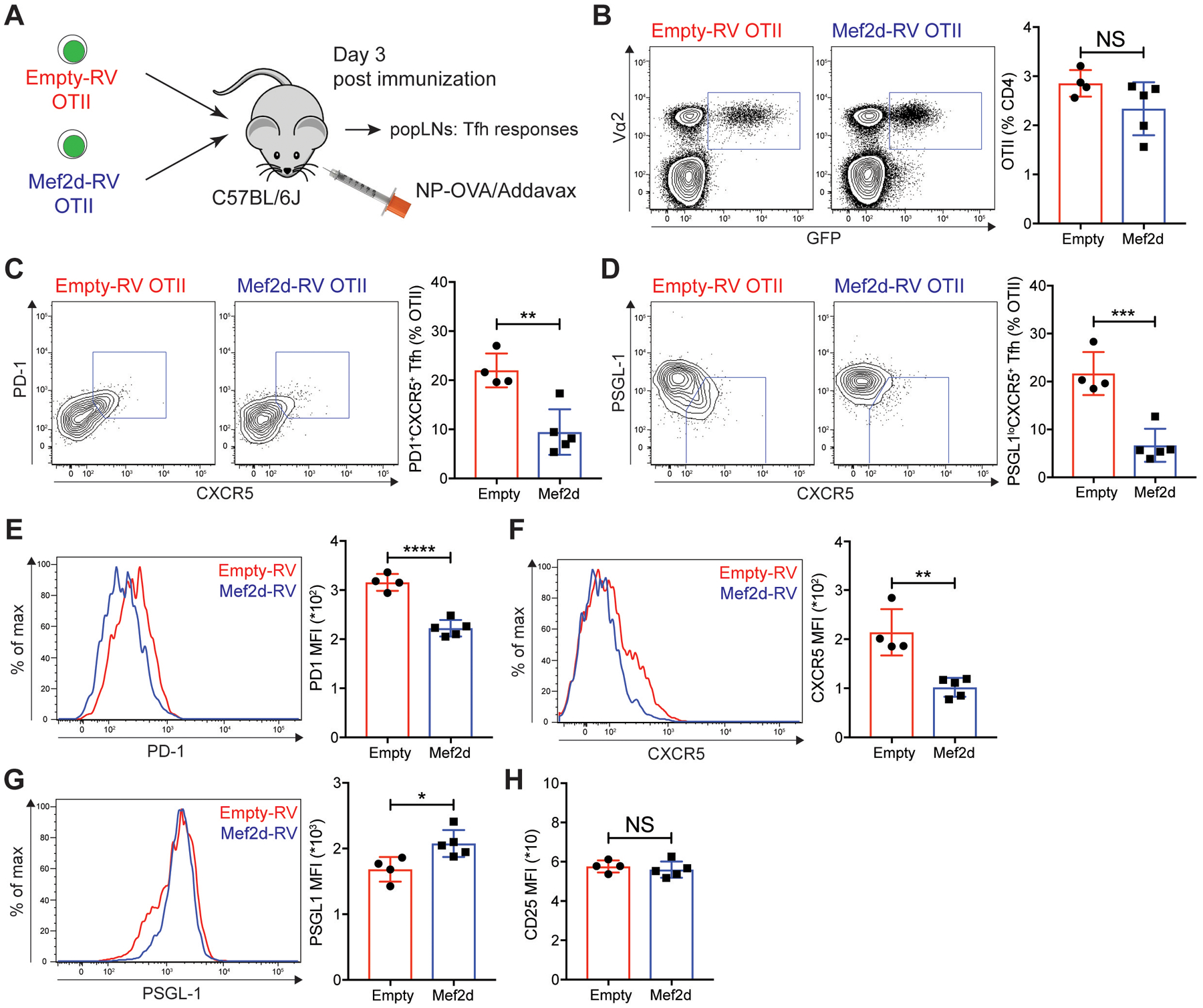
(A) Experimental scheme to analyze Mef2d functions during early Tfh differentiation of CD4 T cells. The same number of empty-RV or Mef2d-RV OTII CD4 T cells were transferred into C57BL/6J mice. Three days after subcutaneous NP-OVA immunization, popLNs were examined for Tfh differentiation of GFP+ OTII CD4 T cells.
(B) Flow cytometry plots of CD4 T cells in the popLNs. Vα2+GFP+ OTII CD4 T cells were gated and quantified.
(C and D) Flow cytometry plots of the transferred GFP+ OTII CD4 T cells with gates indicating PD-1+CXCR5+ (C) and PSGL-1loCXCR5+ (D) Tfh cells. The frequencies of PD-1+CXCR5+ and PSGL-1loCXCR5+ Tfh cells among the GFP+ OTII CD4 T cells were calculated.
(E to G) Overlaid histograms of PD-1 (E), CXCR5 (F), and PSGL-1 (G) of empty-RV (red) and Mef2d-RV (blue) OTII CD4 T cells. MFIs were calculated.
(H) Quantification of CD25 MFIs from empty-RV and Mef2d-RV OTII CD4 T cells.
Representative of two independent experiments with n=4–5 mice per group.
Error bars indicate mean with SD. Statistical significance values were determined using two-tailed Student’s t-test. NS, statistically non-significant; * p <0.05; ** p <0.01; *** p <0.001; **** p <0.0001.
