Fig. 8. Reduced MEF2D expression in CD4 T cells is associated with autoimmune SLE conditions.
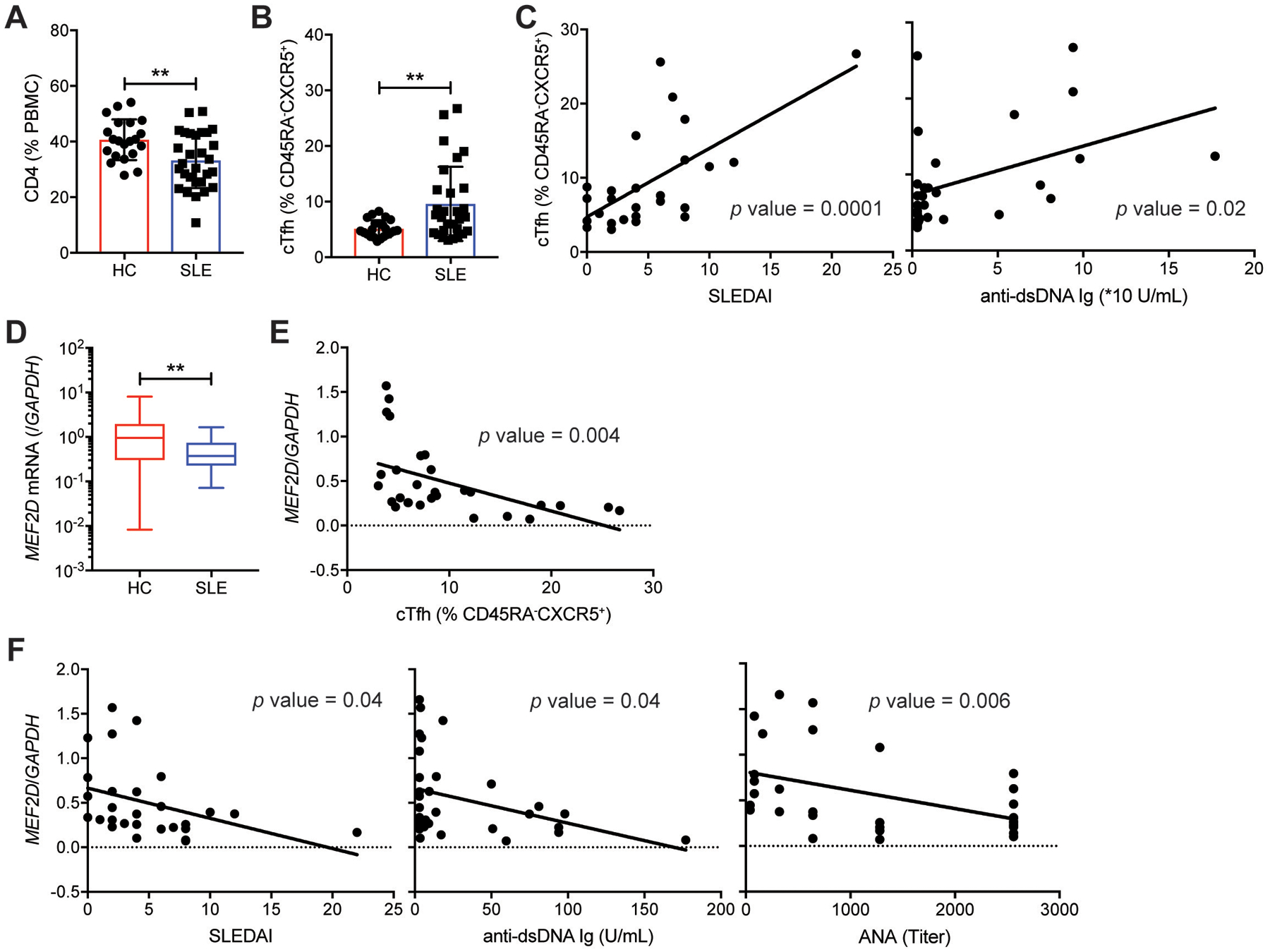
(A) Frequencies of CD4 T cells in PBMC from healthy controls and SLE patients (table S3a).
(B) Frequencies of ICOS+PD-1+ circulating Tfh (cTfh) cells (gating strategy shown in fig. S10A) among peripheral blood CD45RA−CXCR5+ CD4 T cells of healthy controls and SLE patients (table S3a).
(C) Correlations of ICOS+PD-1+ cTfh cell frequency with SLEDAI and anti-dsDNA Ig level in the SLE patients.
(D) MEF2D mRNA measured by qPCR in peripheral blood CD4 T cells obtained from healthy controls and from the SLE patients (table S3a).
(E) Correlation of the MEF2D expression of CD4 T cells with the ICOS+PD-1+ cTfh cell frequency in the SLE patients.
(F) Correlations of the MEF2D expression of the SLE CD4 T cells with SLEDAI, anti-dsDNA Ig, and ANA.
Error bars indicate mean with SD (A and B) and mean with min to max (D). Statistical significance values were determined using two-tailed Student’s t-test (A, B, and D) and Pearson’s correlation analysis (C, E, and F). ** p <0.01.
