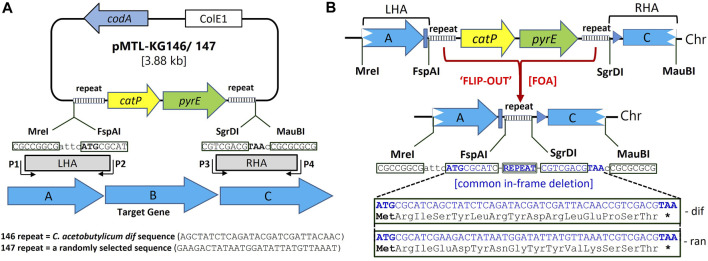
FIGURE 1.
Suicide plasmid, pMTL-KG146/7 for in-frame deletion in clostridia. (A) Both plasmids carry the Gram-negative ColE1 replication region but no Gram-positive replicon. They possess the counter-selection markers codA (cytosine deaminase) and pyrE (orotate phosphoribosyltransferase). The latter is preceded by the positive selection marker catP (chloramphenicol acetyl transferase) with the two genes flanked by identical repeat regions. These comprise a random 29 bp sequence (ran) in the case of pMTL-KG146, whereas pMTL-KG-147 carries the predicted C. acetobutylicum dif sequence. Flanking the repeat sequences are two different pairs of 8 nt recognition sites into which homology arms (HAs) are cloned. These are the sites for the restriction enzymes MreI and FspAI in the case of the left HA (LHA) and SgrDI and MauBI for the right HA (RHA). The DNA, typically between 500 and 1,000 bp, comprising the LHA and RHA are PCR amplified using region-specific primers P1-P4. The P2 primer is designed such that the ATG of the FspAI site equates to the start codon of the gene to be deleted (e.g., gene “B” in the example) whereas primer P3 includes the indicated TAA stop codon that follows the SgrDI recognition site. (B) Following isolation of the double crossover mutant on media supplemented with thiamphenicol and 5FC, colonies are plated on media containing FOA which selects for those cells that have lost the DNA region encoding pyrE::catP as a result of recombination between the two repeat regions. Flip-out of this DNA leads to the presence of a single copy of the repeat region in the genome and the creation of an in-frame deletion in gene “B” encoding a common 15 amino acid peptide. This differs depending on which plasmid is used, pMTL-KG146 or pMTL-KG147.