Figure 2.
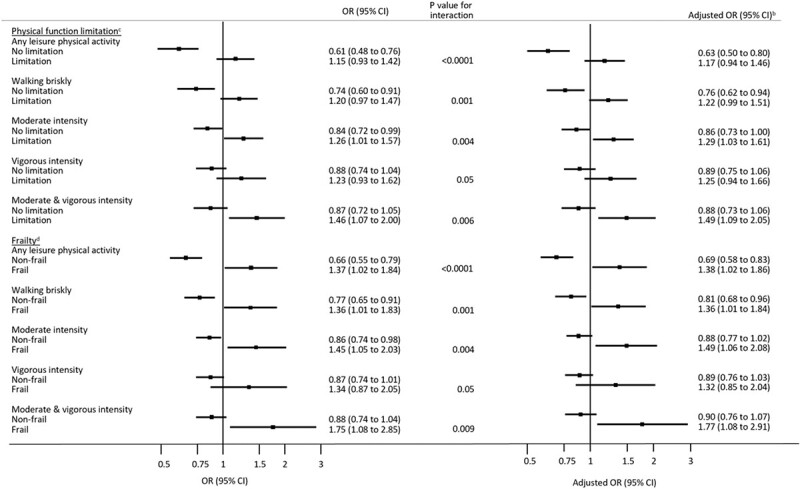
Effect modifications of physical function limitation and frailty on the cross-sectional associationsa between any leisure physical activity and the different types of leisure physical activity and injurious falls in 2016 survey in the 1946–51 born women of the Australian Longitudinal Study on Women’s Health. aCross-sectional association between leisure physical activity and injurious falls were calculated using logistic regression and presented in odds ratios (OR) and 95% confidence intervals (95% CI). Cross-sectional analysis refers to the use of exposure (i.e. leisure physical activity) and outcome (i.e. injurious falls) in 2016 survey (when aged 65–70 years). bAdjusted ORs were presented after adjusting for age, Accessibility Remoteness Index of Australia scale (ARIA+), housing arrangement, education and ability to manage income. cParticipants had a physical function limitation if they responded “limited a lot’ or ‘limited a little’ in their ability to climb one flight of stairs or walk 100 m. dWomen were frail if FRAIL score was greater than 2 points.
