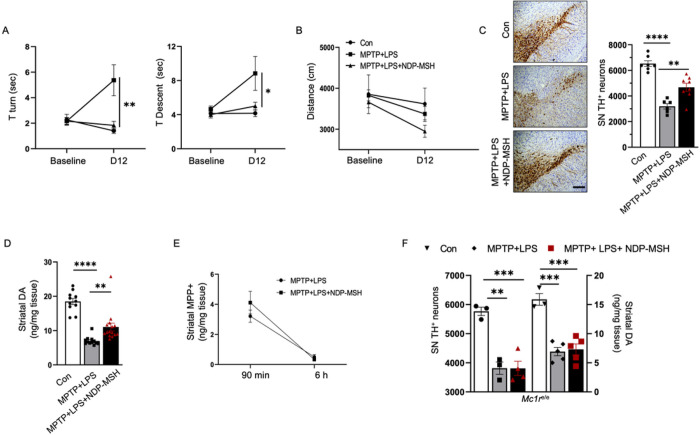
Figure 1. Systemic NDP-MSH treatment protects against MPTP+LPS-induced dopaminergic neurotoxicity.
C57BL/6J mice were treated i.p. with MPTP.HCl (20 mg/kg) and LPS (1 mg/kg) or vehicle (Con) from day (D) 1 to D4 and NDP-MSH (400 μg/kg) or vehicle from D1 to D12 and sacrificed at D12. (A) Pole test for the time taken to turn downward (T turn) on the top of a pole and time taken to climb down (T descent) and (B) open field test to measure the total distance traveled. Two-way ANOVA by Tukey’s post hoc test. *p<0.05, **p<0.01 for MPTP+LPS vs MPTP+LPS+NDP-MSH; n=5–7/group. (C) Representative micrograph and stereological quantification of TH+ cells in SN; n=6–8/group. Scale bar, 100 μm. (D) Striatal dopamine content; n=11–15/group. (E) Striatal MPP+ levels assessed at 90 min and 6 h after treatment with MPTP+LPS with or without NDP-MSH. Two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test, n=3/group.
Mc1re/e mice carrying non-functioning Mc1r were treated with the same paradigm. (F) Stereological quantification of TH+ cells in SN (left y-axis) and striatal dopamine content (right y-axis); n=3–5/group. One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test. **p<0.01; ***p<0.001