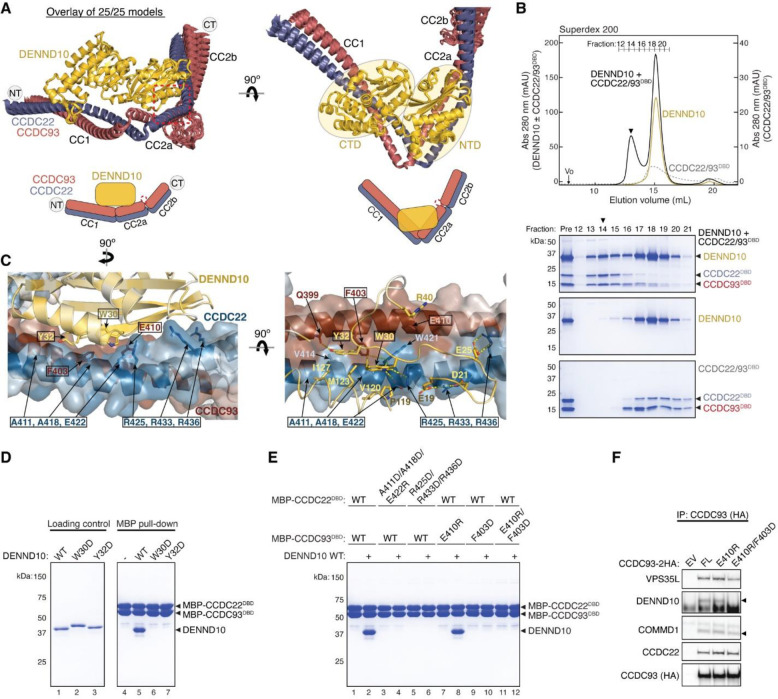
Fig. 6. Structural model of CCDC22-CCDC93 binding to DENND10.
(A) Overlay of all 25 AlphaFold Multimer models and schematic showing DENND10 binding to CCDC22-CCDC93. (B) Gel filtration of DENND10 and CCDC22-CCDC92 DBD, individually and in combination. Coomassie blue-stained SDS-PAGE gels of the indicated fractions are shown. The arrowhead indicates the peak fraction of the trimer. (C) Interaction surface between DENND10 and CCDC22-CCDC93 DBD colored by conservation score using the same scheme shown in Fig. 2. Key interactions are shown as sticks and polar interactions are represented with a dashed yellow line. Residues mutated in this study are outlined with a black box. (D-E) Coomassie blue-stained SDS PAGE gels showing MBP-tagged CCDC22-CCDC93 DBD (200 pmol) pulling down DENND10 (500 pmol). Mutations in corresponding constructs are indicated. (F) Immunoprecipitation of CCDC93 carrying indicated point mutants expressed in HEK293T cells and immunoblotting for the indicated proteins.