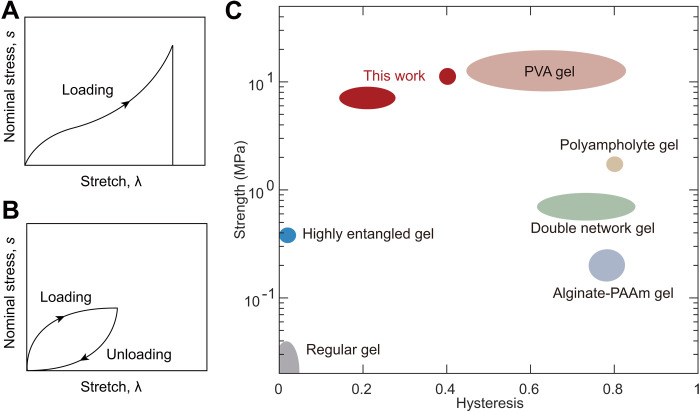
Fig. 2. The strength and hysteresis of representative hydrogels.
(A) Define the nominal stress, s as the applied force divided by the undeformed cross-sectional area; the stretch, λ as the deformed length divided by the undeformed length; and the strength as the nominal stress at rupture. (B) Hysteresis is defined as the ratio of two areas: the area enclosed by the stress-stretch curves of loading and unloading and the area under the stress-stretch curve of loading. (C) Hydrogels are compared on the strength-hysteresis plane. Load-bearing applications often require hydrogels of high strength and low hysteresis (the shaded region), but it has been a challenge to synthesize hydrogels to achieve both simultaneously. PVA hydrogel, poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogels; alginate-PAAm gel, alginate-poly(acrylamide) gel. (15, 17, 20, 22, 23).