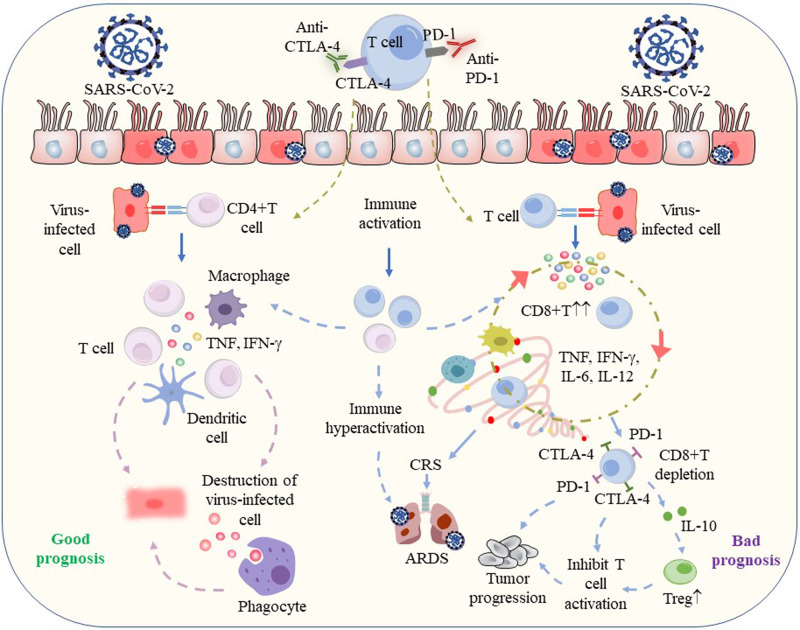
Fig. 1. The possible interplay between SARS-CoV-2 infection and ICI therapy.
The clinical status of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection in patients receiving ICI remains uncertain, but they may have potential interactions. ICI blocks the inhibitory pathway to enhance immunity, increase the release of cytokines, accelerate virus clearance, and ultimately phagocytosis and destroy virus-infected cells. On the other hand, the overactivated immune response may interact with T depletion and cytokine storm in severe COVID-19 patients to induce cytokine release syndrome and accelerate the progression of ARDS [69]. The increased expression of immune checkpoint receptors in turn increases the number of regulatory T cells, which promotes tumor progress [71]. ARDS acute respiratory distress syndrome, COVID-19 coronavirus disease 2019, CTLA-4 cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen 4, CRS cytokine release syndrome, IFN-γ interferon-γ, IL interleukin, PD-1 programmed cell death protein-1, SARS-CoV-2 severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2, Treg regulatory T cells, TNF tumor necrosis factor.