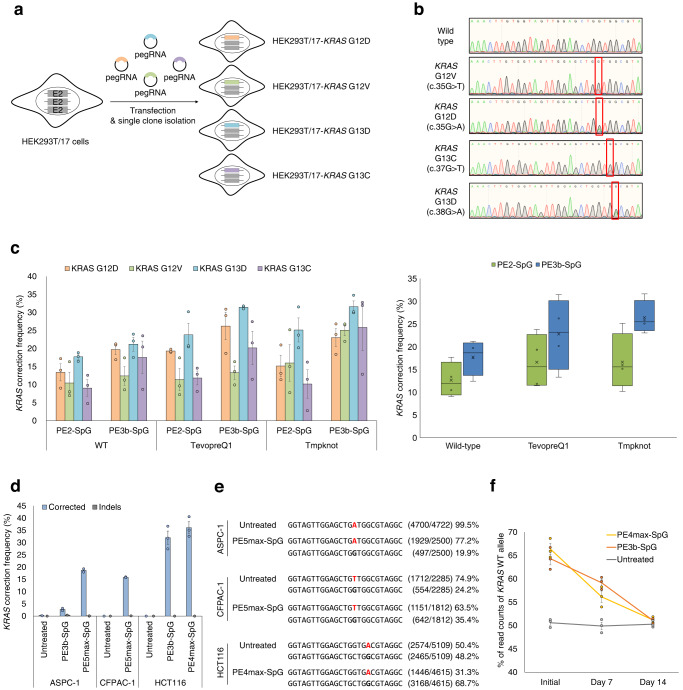
Fig. 3. Correction of endogenous KRAS mutations in HEK293T/17 cells and three human cancer cell lines.
a Schematic for the construction of HEK293T/17 cell lines containing four types of KRAS mutations at endogenous KRAS sites. The pegRNAs and PE2 were delivered into HEK293T/17 cells and single clones were analyzed to obtain HEK293T/17 cells with endogenous KRAS mutations. b Sanger sequencing results for each HEK293T/17 cell line containing endogenous KRAS mutations. c Endogenous KRAS correction frequency in KRAS mutated-HEK293T/17 cells. The universal pegRNAs and epegRNAs were delivered into each KRAS mutated-HEK293T/17 cell by PE2-SpG or PE3b-SpG systems. The KRAS correction frequency was calculated from read counts of NGS sequencing results described in Table S2. Error bars mean s.e.m. of biological triplicate samples (n = 3). d Endogenous KRAS correction in three human cancer cell lines, ASPC-1, CFPAC-1 and HCT116 cells. The KRAS correction frequencies of KRAS heterogenous cell lines, CFPAC-1 and HCT116, were calculated from read counts of NGS sequencing results. Error bars mean s.e.m. of biological duplicate or triplicate samples. e The representative NGS sequencing results of KRAS correction in three human cancer cell lines. KRAS mutations in each cell line (G12D, 12 V, and G13D) were highlighted in red. f The KRAS correction frequency of HCT116 was measured over time. Error bars mean s.e.m. of biological triplicate samples (n = 3).