Figure 4.
Chronically stimulated stem-like CAR-TRM cells sustain a resident memory phenotype in association with epigenetic reprogramming
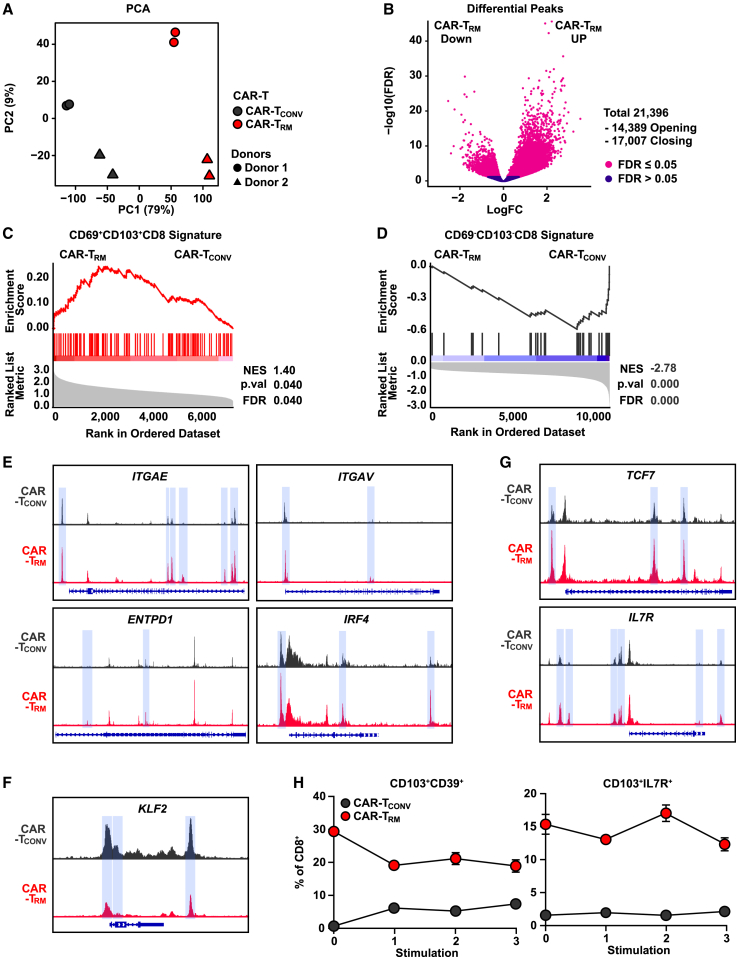
(A) Principal-component analysis of ATAC-seq data.
(B) Volcano plot demonstrating differentially accessible peaks between CAR-TRM and CAR-TCONV CD8+ cells.
(C–G) GSEA showing enrichment of (C) CD69+CD103+CD8+ and (D) CD69−CD103−CD8+ T cell signatures. ATAC-seq tracks of genes associated with (E) resident memory T cells (ITGAE, ITGAV, ENTPD1, IRF4), (F) circulating T cells (KLF2), and (G) stemness (TCF7, IL7R). Differentially accessible regions are highlighted in blue.
(H) M5 CAR T cells were repetitively challenged with AsPC1 cells, and frequencies of resident memory (CD103+CD39+CD8+) and stem-like resident memory (CD103+IL7R+CD8+) T cells are shown over time. Bulk ATAC-seq experiments were performed using manufactured CD8+ CAR T cells from n = 2 healthy donors as biological replicates. Restimulation assays were performed with CAR T cells generated from n = 3 distinct healthy subjects, also serving as biological replicates. Results from one representative donor are shown.