FIGURE 1.
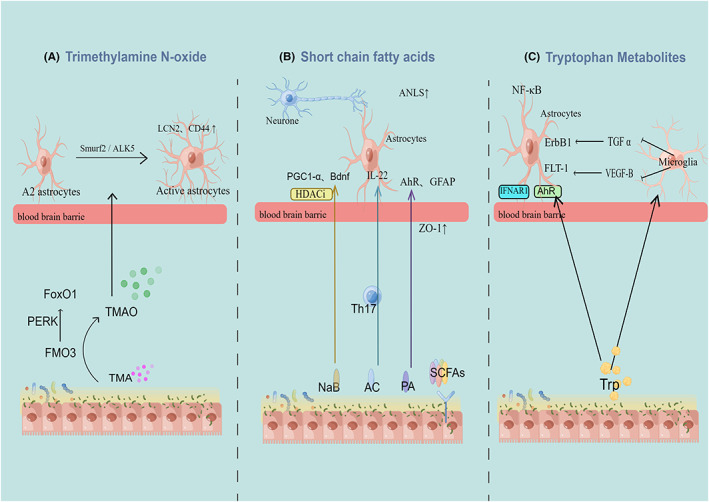
Gut microbiota metabolites drive astrocyte phenotypes. Trimethylamine N‐oxide could increase the number of reactive astrocytes and change the marker of reactive activated LCN2 and CD44 protein through the Smuef2/ALK5 axis. Improvement of short‐chain fatty acids ratio inhibited astrocytic activation and proinflammatory phenotype. The expression of PGC1‐α and brain‐derived neurotrophic factor in female mice was increased by HDACi, while the function of astrocyte mitochondria and ANLS were improved by butyrate (NaB). A significant correlation between acetate and aryl hydrocarbon receptors (AhR) and GFAP expression was observed in male mice, and the BBB structure was improved. Propionate promotes higher glycolysis and mitochondrial respiration in astrocytes and increases IL‐22 expression in male mice. AhR promotes the production of TGF‐α and VEGF‐B by microglia to indirectly regulate the transcriptional program of astrocytes. In combination with tryptophan‐derived metabolites, IFN‐I signaling activates in astrocytes and inhibits neuroinflammation.
