Fig. 2.
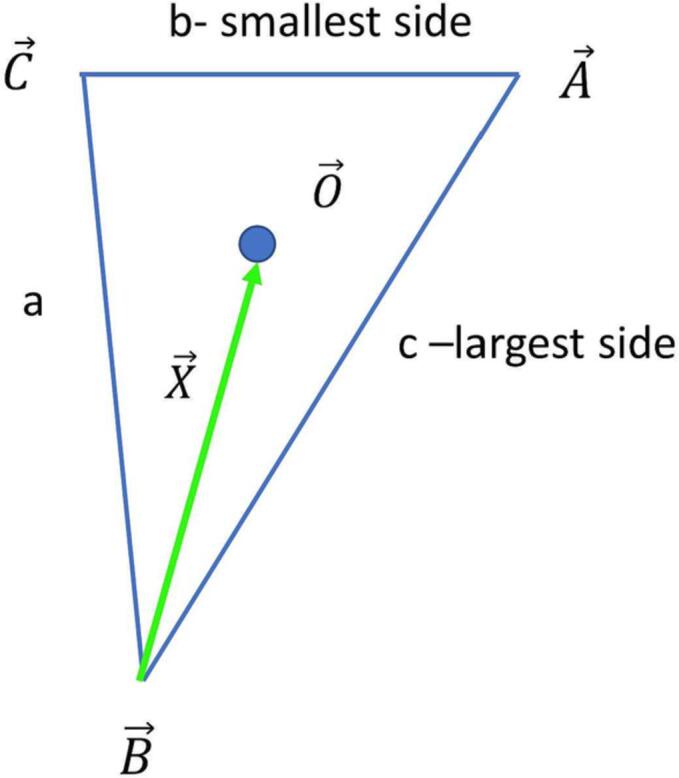
An explication of convenient coordinates for triangles, stemming originally from a correlation analysis. Sides are denoted by , and c, and are opposite the corresponding vertices, , and . The shortest and longest sides are termed b and c respectively. The median of the triangle is constructed as well as the vector from to , which we term “the drop”, . The three coordinates describing the triangle are given by the lengths, X, b and by the angle between and . This angle is always less than or equal to in magnitude. Mirroring the triangle can be represented by changing the sign of this last angle.
