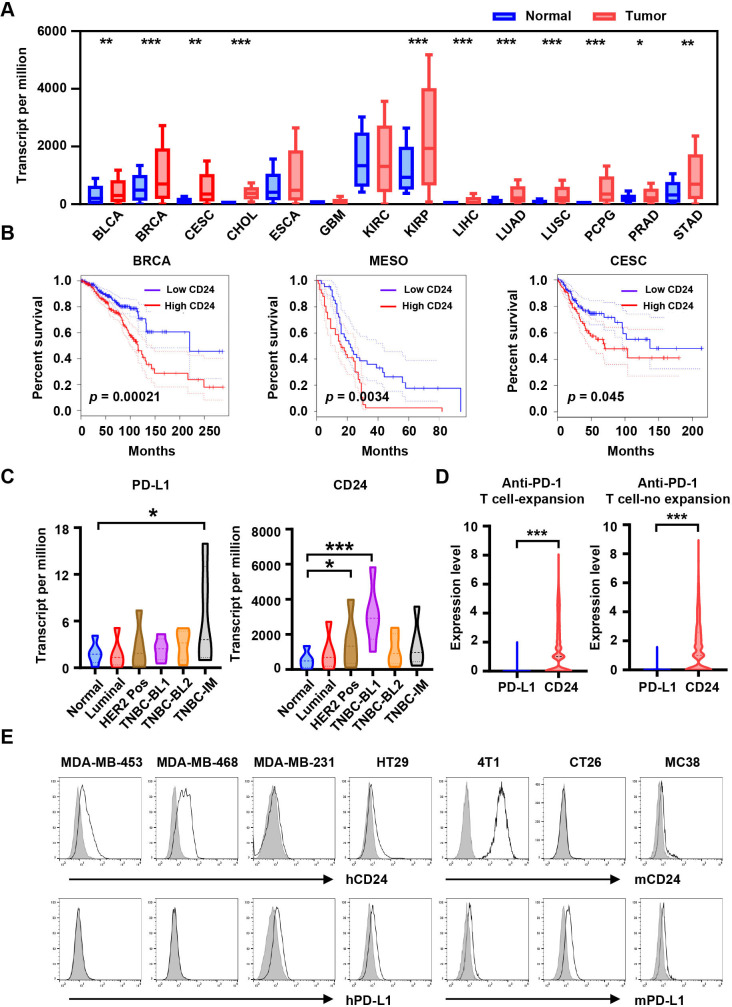
Figure 1.
CD24 is significantly overexpressed in tumors. (A) Expression of CD24 across multiple human cancers (red) compared with corresponding normal tissues (blue) obtained from the UALCAN database. (B) The overall survival curve of human cancers with high and low CD24 expression analyzed by the GEPIA. (C) Expression of PD-L1 and CD24 in BRCA major subclasses via UALCAN database. (D) Expression analysis of PD-L1 and CD24 in human TNBC cells from patients (n=5) where T expansion or no-expansion to anti-PD-1 immunotherapy across single cell sequencing illustrated. (E) Expression of CD24 and PD-L1 on human or mouse tumor cell lines was detected by flow cytometry, gray shading indicates matched isotype controls. Data are presented as means±SEM, and statistical significance was determined by unpaired Student’s t-test. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. BLCA, bladder Urothelial Carcinoma; BRCA, breast invasive carcinoma; CESC, cervical squamous cell carcinoma and endocervical adenocarcinoma; CHOL, cholangiocarcinoma; ESCA, esophageal carcinoma; GBM, glioblastoma multiforme; GEPIA, gene expression profiling interactive analysis; KIRC, kidney renal clear cell carcinoma; KIRP, kidney renal papillary cell carcinoma; LIHC, liver hepatocellular carcinoma; LUAD, lung adenocarcinoma; LUSC, lung squamous cell carcinoma; MESO, mesothelioma; PCPG, pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma; PD-1, programmed cell death protein 1; PD-L1, programmed death ligand 1; PRAD, prostate adenocarcinoma; STAD, stomach adenocarcinoma; TNBC, triple negative breast cancer.