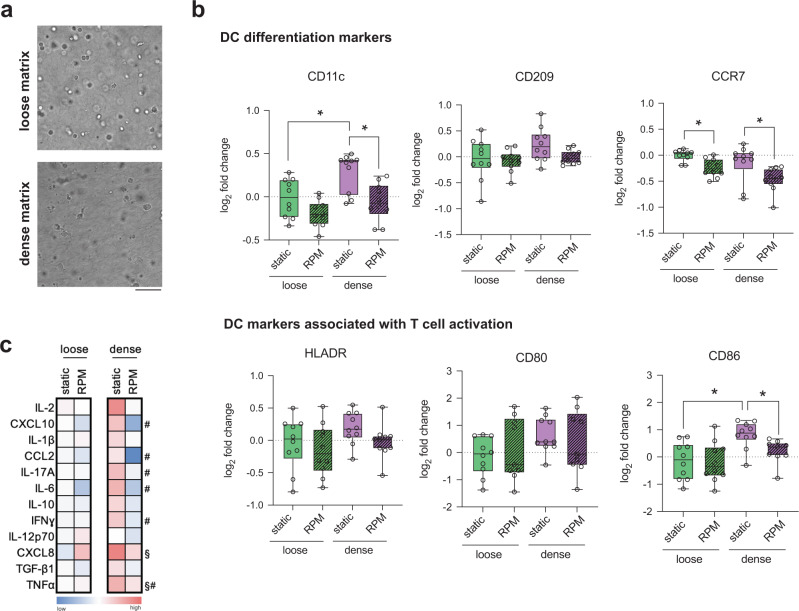
Fig. 2. Quantitative analysis of iDC surface markers and cytokines.
Monocyte-derived iDCs were cultured for 3 days under static conditions or on the RPM in loose and dense matrices. a Representative brightfield images of iDCs cultured in loose and dense matrices under static conditions. The scale bar represents 100 µm. b Analysis of surface markers associated with differentiation, namely, CD11c, CD209, and CCR7, and markers associated with T-cell activation, namely, HLADR, CD80, and CD86, using flow cytometry. The log2-fold change in geometric mean fluorescence intensity (gMFI) was calculated relative to samples cultured in loose matrices under static conditions. c Heatmap of the log2-fold change in cytokine secretion by iDCs cultured in loose and dense matrices under static and RPM conditions. The log2-fold change in the median concentration of cytokines (pg/mL) was calculated relative to the cytokine concentration secreted by iDCs in loose matrices under static conditions. Experiments were performed with at least four replicates. The box and whiskers graphs used have the center line at the median value. The upper and lower bounds of the box extend from the 25th to 75th percentiles, and the whiskers are plotted to the minimum and maximum values. * indicates significance at p ≤ 0.05. For the heatmap, # indicates a significant p ≤ 0.05 of samples in dense matrices under RPM conditions compared to dense matrices under static conditions. § indicates significant p ≤ 0.05 of samples in dense matrices at static conditions compared to loose matrices at static conditions.