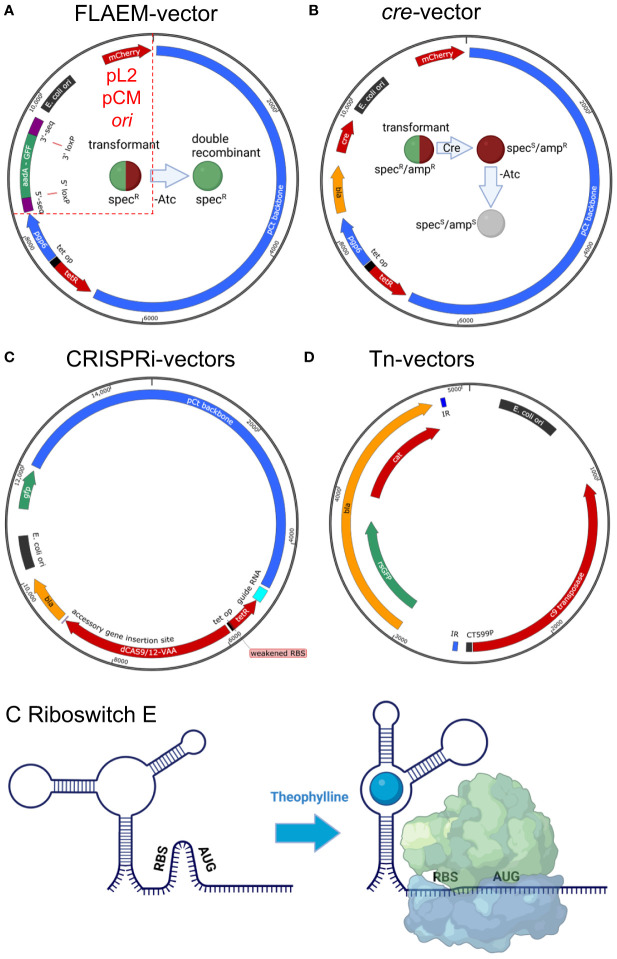
Figure 2.
Updates to the chlamydial genetics toolbox. (A) Allelic exchange (FLAEM) utilizes the pSUmC-4.0 vector to obtain recombinant gene deletion mutants (Keb and Fields, 2020). 5′- and 3′- gene sequences from the targeted gene are cloned flanking the resistance gene (aadA) and reporter gene (gfp) which are expressed from their own promoters. Upon transformation, the strain exhibits red and green fluorescence and resistance to spectinomycin. Removal of aTc to halt pgp6 expression creates a suicide plasmid scenario promoting homologous recombination under spectinomycin selection. A double-recombination event will result in a strain with green fluorescence and spectinomycin resistance. A single-recombination event is noted by a red and green fluorescent bacterium. Mini-shuttle vectors would only possess sequences defined by the red dashed lines and would include the native plasmid origin of replication (Fields et al., 2022). (B) The cre-bearing vector, pSU-CRE, can then be transformed into the strain and selected via ampicillin yielding a red and green fluorescent strain resistant to spectinomycin and ampicillin. Expression of Cre will mediate excision of the loxP-flanked aadA-GFP cassette generating a spectinomycin sensitive, red fluorescent bacterium. Removal of aTc can then be performed to cure the plasmid allowing for complementation of the mutant or construction of additional mutants. The cured strain will be sensitive to ampicillin and not fluorescent. (C) A base CRISPRi vector is shown with the guide RNA location shown in light blue (Ouellette et al., 2021). Guide expression is constitutive owing to a dnaK P, and expression is isolated from downstream elements via an rrnB1 terminator sequence. Either dcas9 or dcas12 can be used for gene silencing, and expression of the dCas9/12 encoding an SsrA VAA degradation tag is controlled by the tet promoter. Accessory genes may be inserted 3′ of the dcas gene to make transcriptional fusions for complementation studies. (D) For transposon mutagenesis, a pUC-based suicide vector is used carrying the himar1 c9 transposase and either bla [used for C. trachomatis (LaBrie et al., 2019)] or gfp and cat [for C. muridarum (Wang et al., 2019)] in the transposon region defined by the inverted repeats (IR, shown in blue). (E) A generic riboswitch is shown to represent the synthetic riboswitch E, which is responsive to theophylline (Grieshaber et al., 2022). In the absence of theophylline, the 5′ UTR folds to block the RBS. Binding of theophylline changes the folding of the 5′ UTR revealing the RBS and allowing for binding of the ribosome and translation. To create a “tighter” expression system, the riboswitch can be inserted downstream of the tet promoter (tet systems are shown in A–C) to allow for gene regulation via aTc induction and translational regulation via theophylline (not pictured). Vector maps were drawn with SnapGene, and sizes are approximate. Vectors are not drawn to scale. Images were drawn with BioRender.com.