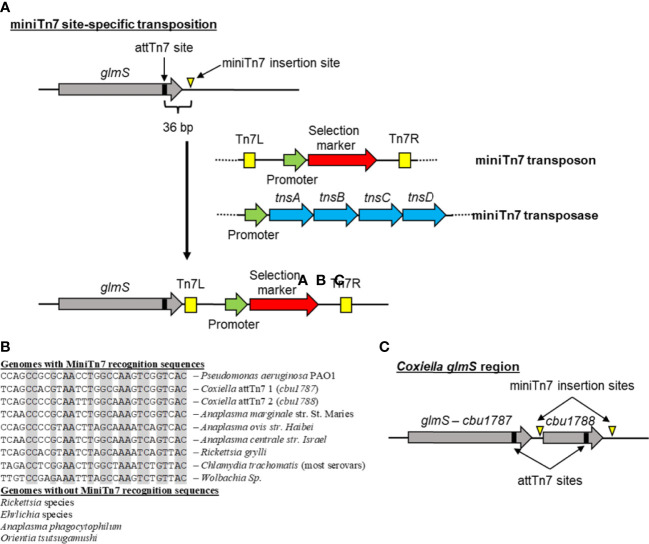
Figure 4.
MinTn7 transposition in bacteria. (A) Schematic of site-specific miniTn7 transposition into the region downstream of the glutamine-fructose-6-phosphate gene (glmS). The glmS gene has a 30-bp attTn7 site in the end of it that is recognized by the miniTn7 transposase (consisting of the TnsA, TnsB, TnsC, and TnsD proteins). Subsequent miniTn7 insertion occurs 36 bp downstream of the attTn7 site. This transposition system utilizes two plasmids, one containing the miniTn7 transposon with a selectable marker and the second containing the miniTn7 transposase genes. (B) Alignment of predicted miniTn7 attTn7 sites in different obligate intracellular bacteria compared with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. No predicted attTn7 sites were identified in Rickettsia, Ehrlichia, or Orientia species and even though other Anaplasma species have an attTn7 site, these were not found in A. phagocytophilum. Gray boxes indicate conserved sequences. (C) Schematic of the C. burnetii glmS region. Due to a duplication event between the end of cbu01787 and cbu01788, C. burnetii has two different attTn7 sites allowing for integration into either site.