FIGURE 7.
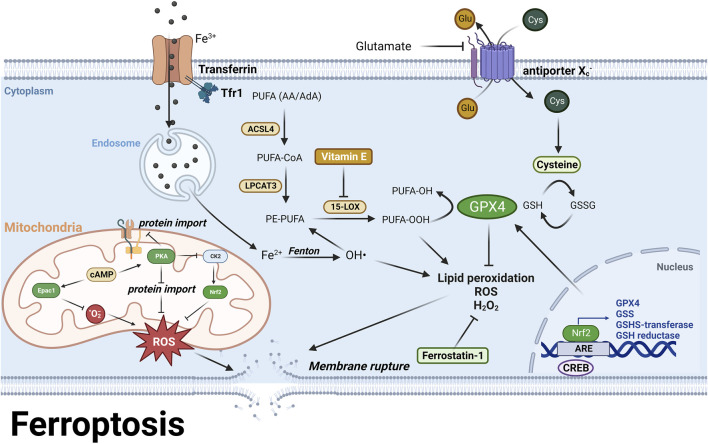
PUFA are stepwise oxidized into lipid hydroperoxides, PUFA-OOH by ACSL4, LPCAT3, and 15-LOX (Kagan et al., 2017; Li and Li, 2020). GPX4 uses GSH as a substrate to catalyze lipid hydroperoxides into hydroxy derivatives, limiting lipid peroxidation (Lewerenz et al., 2013). Excessive glutamate or System Xc-inhibition causes GSH depletion and attenuates GPX4 activity, leading to lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis (Bannai and Kitamura, 1980). Moreover, iron overload generates hydroxyl radicals via Fenton reaction, which also contributes to lipid peroxidation (Yang et al., 2016). Epac1 inhibition reduces ROS levels and lipid peroxidation by decreasing mitochondrial superoxide (Musheshe et al., 2022), while PKA suppresses mitochondrial activation and ROS production via inhibiting protein import (Ishii et al., 2019). In the meantime, PKA indirectly inhibits Nrf2 via outcompeting with Nrf2 regulator CK2. In addition, CREB regulates GPX4 transcription to prevent ferroptosis (Wang et al., 2021). These findings highlight the role of cAMP signaling in preventing ferroptosis via both PKA and mitochondrial Epac. For further details, see text.