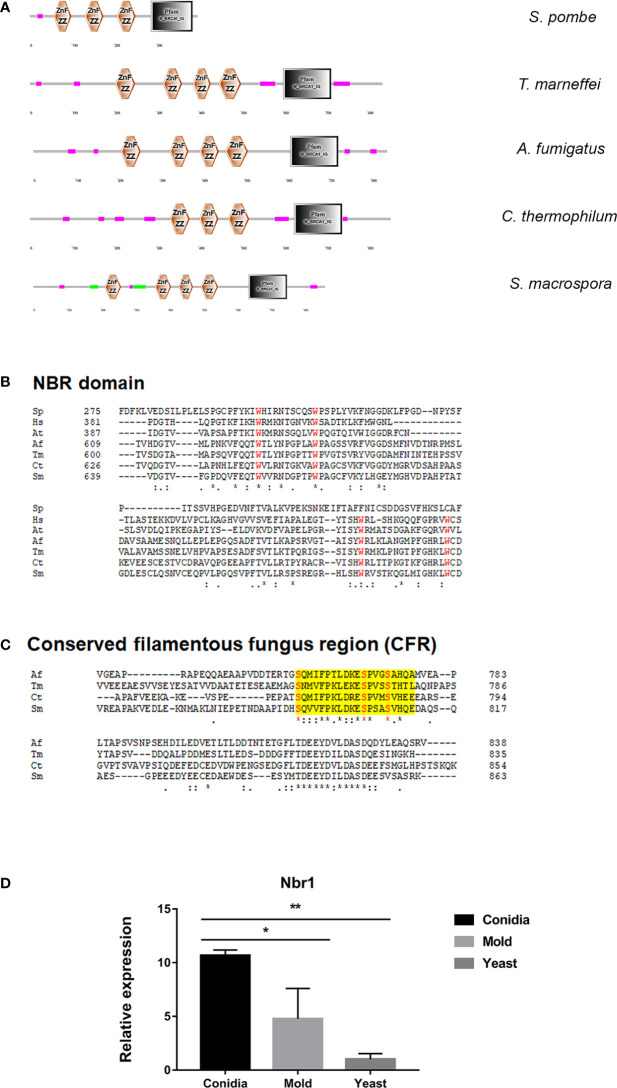
Figure 11.
The antigenic protein shows high homology with the conserved autophagy receptor Nbr1. (A) The protein architecture of Nbr1 homologs in fungal species is shown: Magenta box = low complexity region; Green box = coiled-coil region; Black box = N_BRCA1_IG (Ig-like domain from next to BRCA1 gene, PF16158); Znf ZZ = ZZ-type zinc finger domain. (B) Alignment of the Nbr domain of the following species: Sp = S. pombe (NP_001342955.1); Hs = Homo sapiens (Q14596.3); At = Arabidopsis thaliana (OAO97459.1); Sm = Sordaria macrospora (XP_003346367.1); Ct = Chaetomium thermophilum (XP_006696593.1); Tm = T. marneffei (XP_002152652.1); Af = A. fumigatus (XP_755022.1). Red font highlights the four conserved tryptophan (FW) residues typical for this Nbr1 domain. (C). The conserved fungal region (CFR) at the C-terminal was found in Tm Nbr1 and other filamentous ascomycetes. Yellow shading depicts the CFR, and red font highlights the 3 conserved serine (S) residues. (D) TmNbr1 gene expression was analyzed in T. marneffei grown in yeast, mold, or conidia. Strains were grown, RNA was prepared, and gene expression was analyzed as described in the legend of Figure 3 . The experiment was performed in three biological replicates. Error bars indicate standard deviation. Statistically significant values (* P≤ 0.05, ** P≤ 0.01) are indicated.