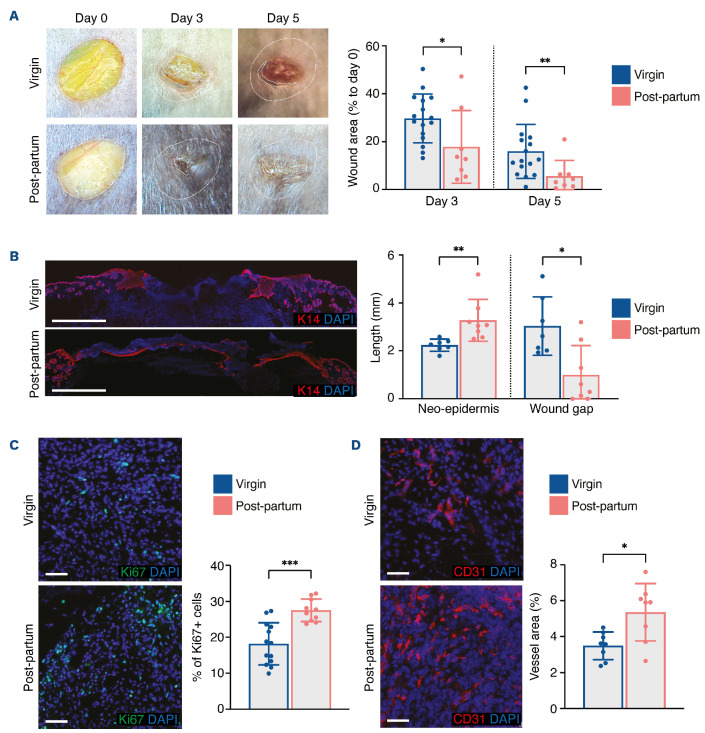
Figure 1.
Improvement of skin wound healing is sustained in post-partum mice. (A) Representative images of wounds at days 0, 3, and 5, and planimetry of wound area at each time point relative to the original wound area. (B) Representative images and measurement of anti-K14 labeling of neo-epidermal tongues and wound gap at day 5. (C) Representative images and quantification of Ki67+ cells in the wound bed at day 5. (D) Representative images of CD31+ cells and quantification of vessel area in the wound bed at day 5. Scale bars represent 1000 mm (B) or 50 µm (C, D). In (B-D), nuclei were counterstained with DAPI. In (A-D), four 6-mm excisional wounds were performed in virgin mice (n=4) or post-partum mice (n=2). Data are presented as means with standard deviations and individual values. Statistical analyses were performed with two-tailed t tests with the Welch correction whenever required (A [day 3], C-D) or Mann-Whitney test (A [day 5], B). *P<0.05; **P<0.005; ***P<0.0005.