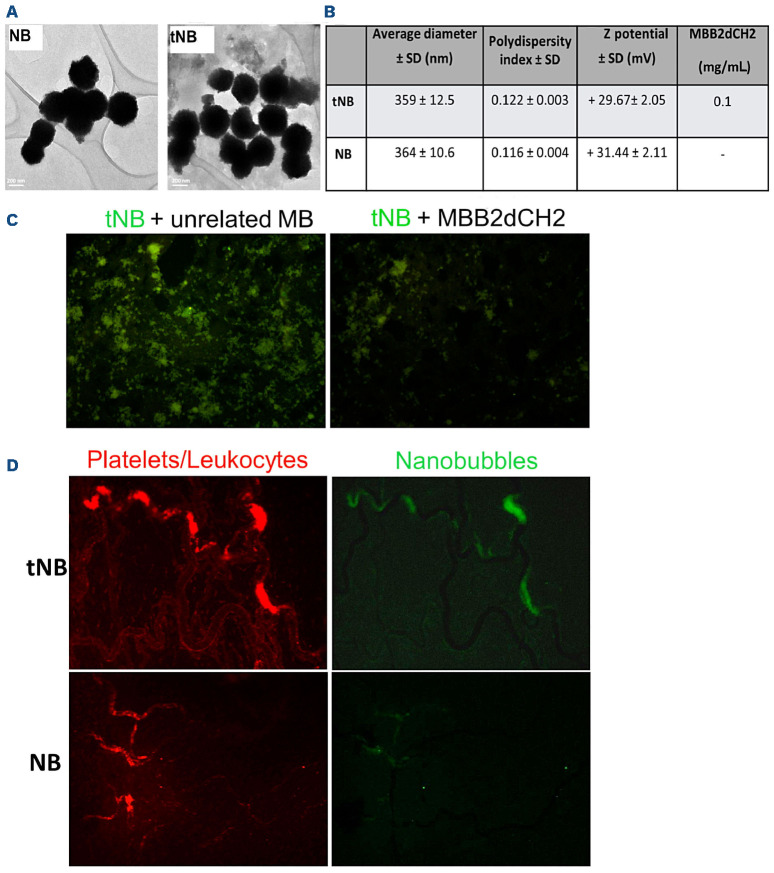
Figure 2.
Physico-chemical characteristics and binding of nanobubbles to thrombi. (A) Transmission electron microspcopy (TEM) images showing similar morphology of untargeted nanobubbles (NB) and targeted NB (tNB); (B) average size, size distribution (polydispersity index) and particle charge (Z potential); MBB2DCH2 denotes the recombinant CH2-deleted scFv-Fc miniantibody against the DI domain of (32-GPI. (C) In vitro binding of tNB to patient’s thrombus sections and inhibition by soluble MBB2DCH2. Tissue sections were pre-incubated either with MBB2DCH2 or an unrelated recombinant antibody (unrelated MB) (100 mg/mL) for 15 minutes (min) prior to exposure to tNB containing 10 mg/mL MBB2DCH2 for further 60 min; (D) in vivo co-localization of platelets and leukocytes (stained in red with rhodamine 6G) and NB loaded with coumarin 6 (green) on thrombi induced in rats by administration of antibodies to (32-GPI. SD: standard deviation.