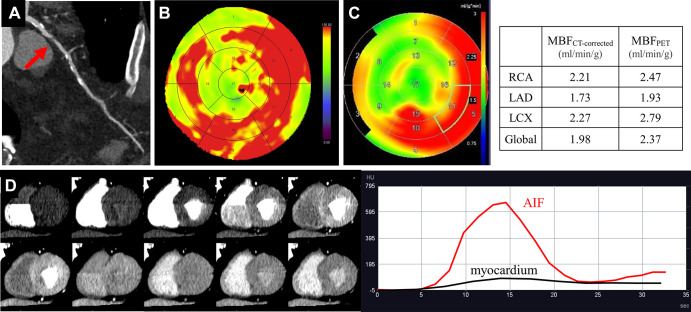
Figure 3:
Images in a 72-year-old man with diabetes and hyperlipidemia. (A) Coronary CT angiographic image shows severe stenosis (red arrow) in the proximal portion of the left anterior descending artery (LAD). Both the (B) MBF CT map and (C) MBF PET map demonstrate similar distribution of abnormal perfusion in the anteroseptal wall and apex corresponding to the LAD stenosis. (D) The dynamic CT perfusion (CTP) images and time-attenuation curve obtained with dynamic CTP are demonstrated. AIF = arterial input function, LCX = left circumflex artery, MBF = myocardial blood flow, MBFCT = CT-derived MBF, MBFCT-corrected = CT-derived MBF after correction with the fitting curve, MBFPET = PET-derived MBF, RCA = right coronary artery. (Reprinted, with permission, from reference 12.)