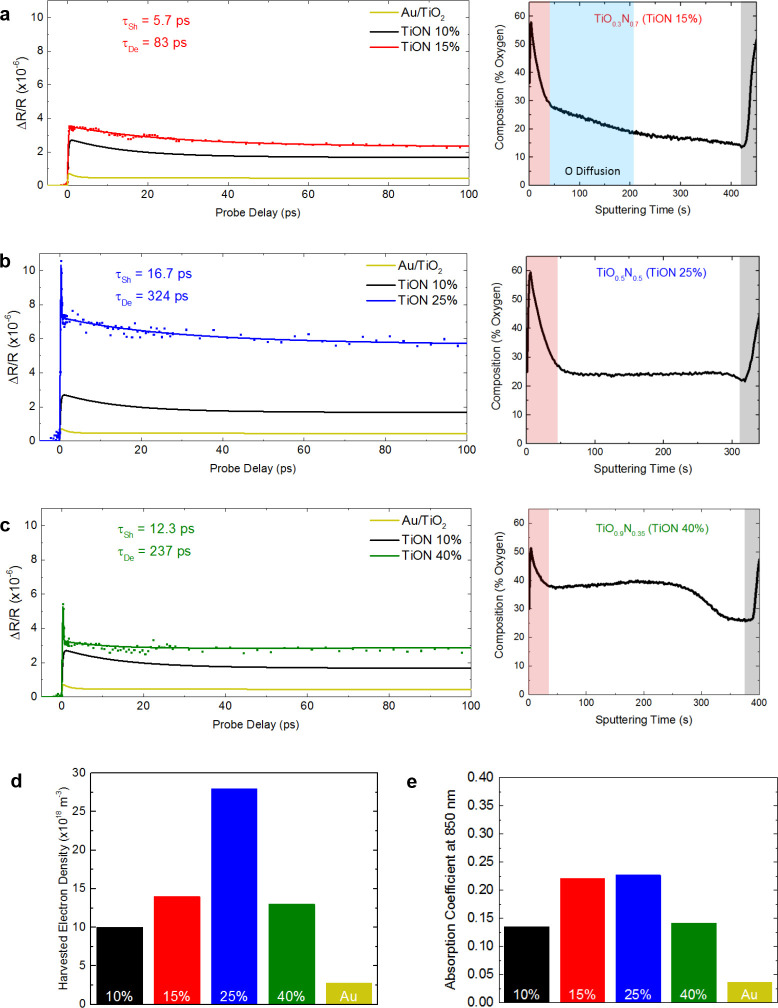
Figure 5.
Optimization of hot electron injection by tailoring the oxygen content in TiON thin films. (a–c) Differential reflectivity following a 5 mW pump pulse (left) and oxygen composition (right) measured with ToF-SIMS for films with increasing oxygen content TiON 15% (a), TiON 25% (b), and TiON 40% (c). Each film exhibits a higher differential reflectivity than both the Au/TiO2 and TiON 10% films over the entire temporal range. With sufficiently high oxygen included in the TiON films (25% and 40%) no postdeposition oxygen diffusion is detected as is seen in the TiON 10% and TiON 15% films. This more uniform interface results in more energetic electrons reaching the TiO2–x interface and the emergence of an ultrafast peak. (d) Maximum free carrier concentration in the TiO2–x determined via the fitting of differential reflectivity measurements. (e) Absorption coefficient at the pump wavelength (850 nm) for each film. It is clear that the strong enhancement in electron harvesting observed in TiON 25% cannot be explained simply by an increase in absorption.