Fig. 7.
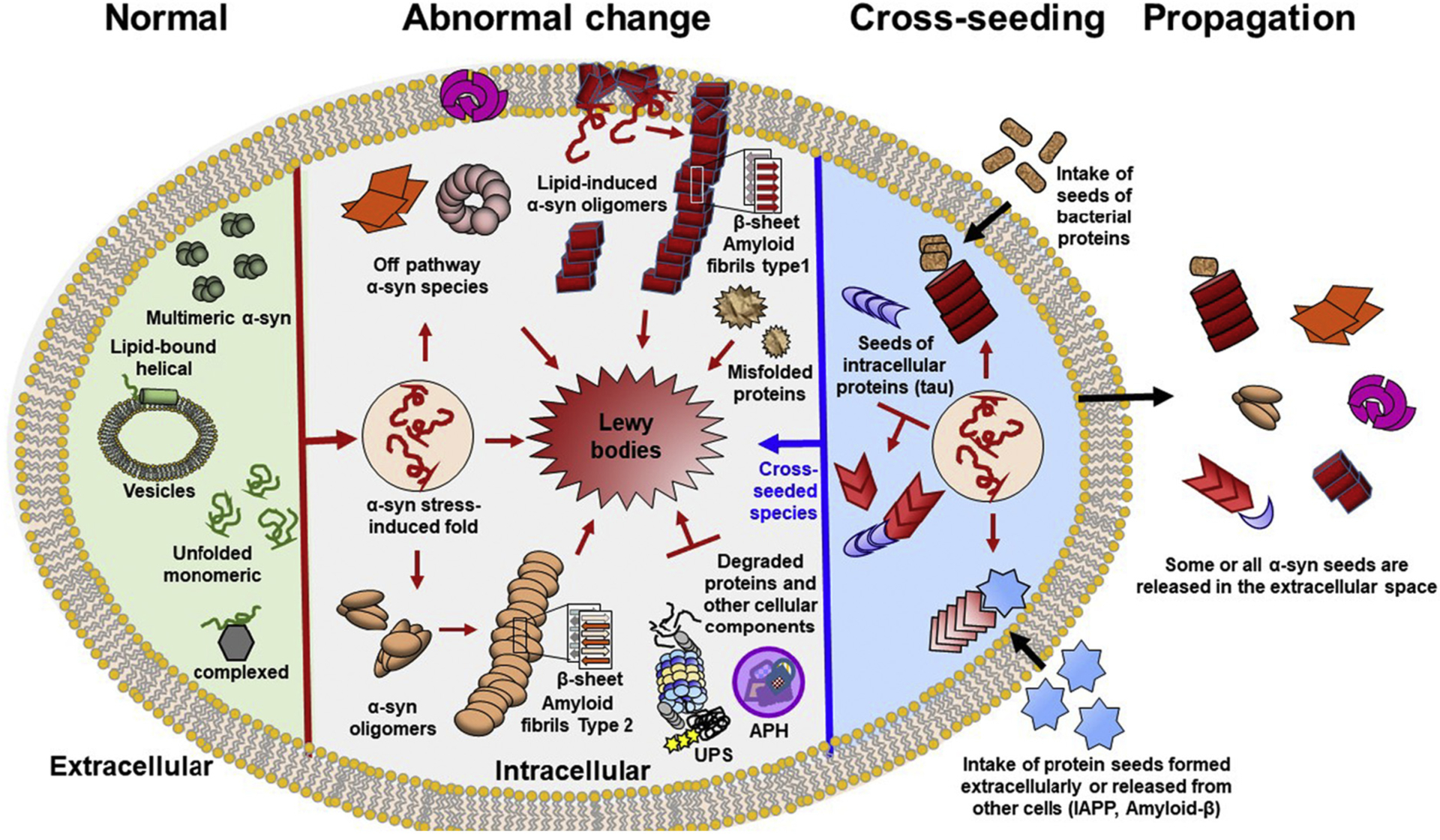
Schematic diagram of α-synuclein multimerization and Lewy body formation. For simplicity a single cell is shown. Homo- and hetero- multimers of α-synuclein are formed in both physiological (green) and pathological conditions (pink-red). Different shapes depict the structural heterogeneity of the pathogenic species. Cross-seeds are colored in blue and brown. Normally, α-synuclein is natively unfolded protein that adopts different conformations. This structural plasticity facilitates binding to many different proteins allowing α-synuclein to perform different functions. α-Synuclein also binds to vesicle membranes as a α-helical monomer. Multiple different stressors favor conformations that are prone to pathogenic multimerization. These factors include protein mutations, abnormal PTMs, metabolites, change of lipid composition, environmental pollutants (pesticides), and reactive oxygen species. Other triggers of multimerization are impaired ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS) and chaperone function, as well as, dysregulation of autophagy (APH) and mitochondrial oxidative stress. The pathogenic multimerization results in off-pathway oligomers, or on- pathway oligomers. The on- pathway amyloid oligomers further grow into β-sheet-rich amyloid fibrils. Additionally some types of lipids can cross-seed the abnormal multimerization of α-synuclein (on- or off- pathway oligomers). Similar to lipids, other aggregation-prone proteins (tau, bacterial, Aβ, IAPP, prion etc) can cross-seed the multimerization of α-synuclein converting native α-synuclein and other cellular proteins into pathogenic entities. The end product of α-synuclein multimerization is Lewy bodies, which are large cellular inclusions with complex structures containing other multiple other components in addition to α-synuclein. The role of the non-synuclein components that can cross-seed α-synuclein multimerization and facilitate LB formation are poorly understood.
