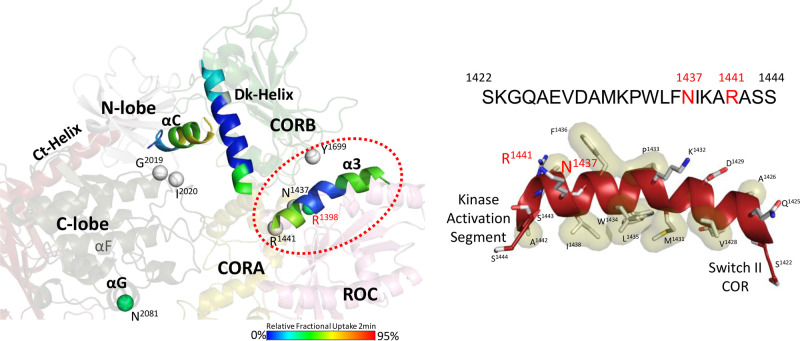
Figure 2. Helical Motifs in LRRK2RCKW drive the crosstalk between domains in LRRK2.
The helical motifs in the CORB domain and the C-terminal (Ct) helix flank the kinase domain while the α3ROC Helix in the ROC domain dominates the interface between the ROC and CORB domains, where many PD mutations are localized (red circle). The solvent exposure of each helix is illustrated by color coding based on HDX-MS data. (Left) The α3ROC helix is very hydrophobic and creates an interface with the CORB domain on one surface and is docked up against Switch II on the other surface (Right).