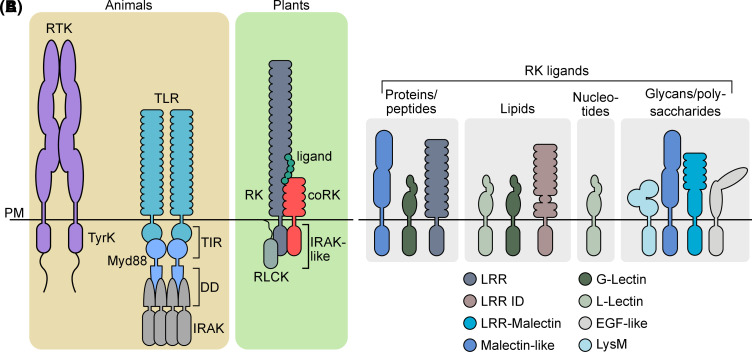
Figure 1. Architecture of selected transmembrane signaling proteins.
(A) Comparison of selected single-pass transmembrane receptors from animals and plants. RTKs consist of ligand binding extracellular domains tethered to intracellular tyrosine kinase domains and have long C-terminal tails involved in the recruitment of signaling partners. Activated TLRs form a large multimeric complex called the Myddosome. The complex is nucleated by TIR and DD of the protein, Myd88. Myd88 DD recruits multiple IRAKs that execute downstream signaling. Plant RKs consist of extracellular ligand-binding domains directly tethered to a cytoplasmic IRAK-like protein kinase domain and typically function with a co-receptor (coRK) and RLCKs that activate downstream signaling. An LRR-RK complex is shown as an example. (B) Plant RKs have diverse ectodomains that perceive a broad range of endogenous and exogenous ligands.