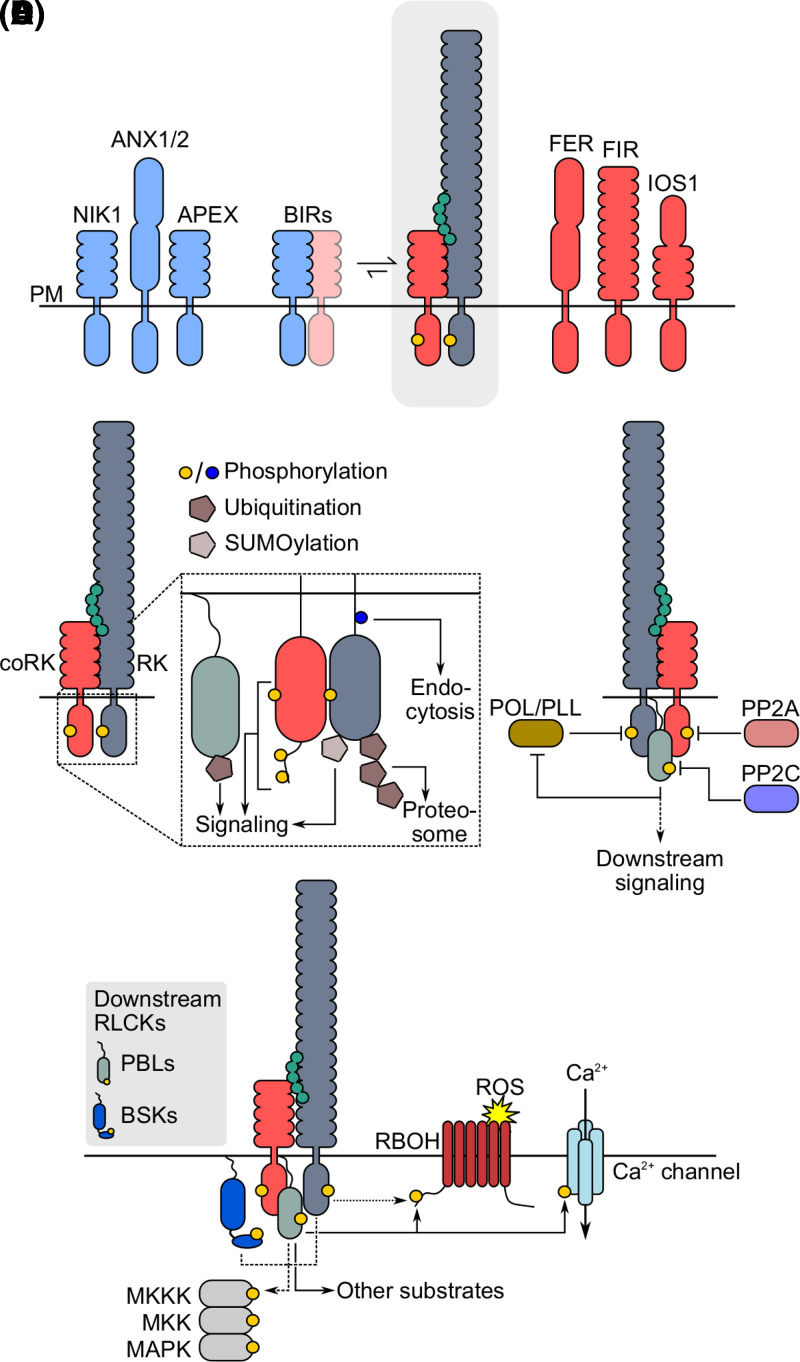
Figure 2. Activation and regulation of RK-mediated signaling.
(A) Receptor complex formation is triggered by ligand binding (grey box) and is positively (red) and negatively (blue) regulated by several accessory RKs through different mechanisms. Regulatory RKs shown function in PAMP-triggered immune signaling. (B) RK cytoplasmic domains are post-translationally modified following ligand perception. Cytoplasmic domain phosphorylation is essential to activate downstream signaling (yellow) and controls RK endocytosis (blue). Poly-ubiquitination leads to RK degradation. Mono-ubiquitination of BIK1 activates immune signaling. SUMOylation of multiple RKs positively regulates downstream responses. (C) Regulation of LRR-RK mediated signal activation by protein phosphatases. (D) Downstream signaling is primarily executed by RLCKs from the PBL and BSK families. PBLs directly activate RBOHD and Ca2+ channels (solid arrows). RBOH are directly activated by ligand-binding receptors in some contexts (dotted arrow). MAPK cascades are activated by RKs, PBLs, or BSKs depending on the receptor complex (dotted arrows). LRR-RKs are shown as representative RKs in B and D. See text for details.