Table 5.
Repurposed drugs
| Drug/structure | Original indication | Target | Organism | Repurposed/progress | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Isotretinoin 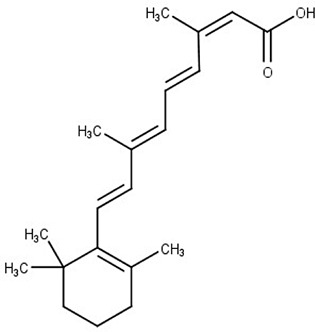
|
Acute acne | Polyamine permease | T. cruzi | Effectiveness in animal model | Reigada et al. (2017) |
Cisapride 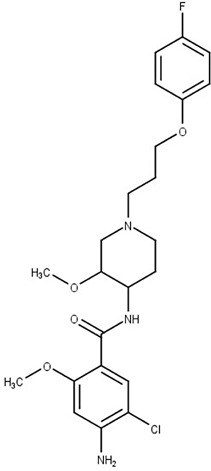
|
Gastroesophageal reflux | Polyamine permease | T. cruzi | Evaluation in T. cruzi clinically relevant forms | Dietrich et al. (2018) |
Miglitol 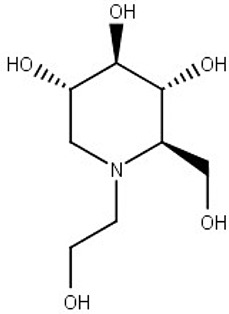
|
Diabetes mellitus type 2 | N-glycan biosynthesis (predicted) |
L. amazonensis L. infantum |
Effectiveness in animal model | Chavez-Fumagalli et al. (2019) |
Eflornithine (6) 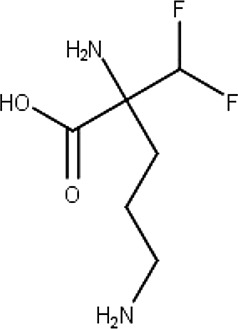
|
Cancer | Polyamine metabolism | T. brucei | Human African trypanosomiasis | Burri and Brun (2003) |
Nifurtimox (2) 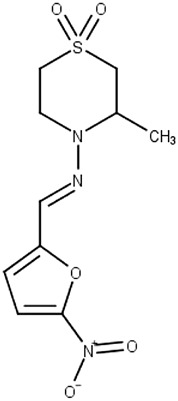
|
Chagas disease | Macromolecules | T. brucei gambiense | Second stage human African trypanosomiasis, in combination with eflornithine | Priotto et al. (2009); Hall et al. (2011) |
Fexinidazole (7) 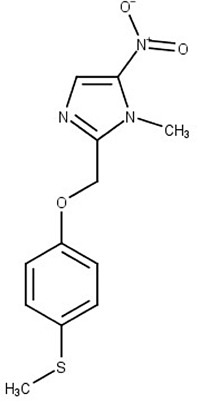
|
Broad-spectrum antimicrobial agent | DNA |
T. brucei gambiense T. cruzi |
Phase III clinical trials for African trypanosomiasis Clinical trials for Chagas disease |
Raether and Seidenath (1983); Deeks (2019); Bahia et al. (2012); Francisco et al. (2016) |
Amphotericin B (12) 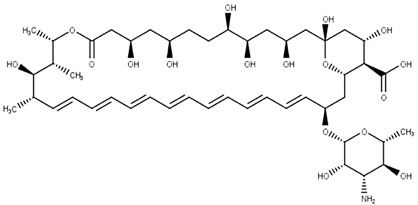
|
Antifungal agent | Ergosterol | Leishmania spp. | Visceral leishmaniasis | Meyerhoff (1999); Roberts et al. (2003) |
Paromomycin (11) 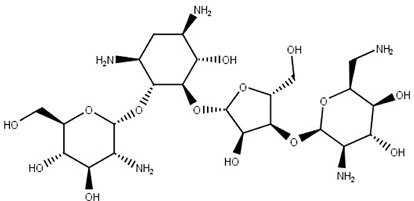
|
Antibiotic (bacteria, protozoa and cestodes) | Cytoplasmic and mitochondrial protein synthesis | Leishmania spp. | Visceral and cutaneous leishmaniasis | Davidson et al. (2009); Jhingran et al. (2009); Jain and Jain (2013) |
Miltefosine (10) 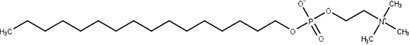
|
Cutaneous cancer | Lipid biosynthesis | Leishmania spp. | Visceral and cutaneous leishmaniasis | Sindermann et al. (2004); Dorlo et al. (2012); Ortega et al. (2017); Pinto-Martinez et al. (2018) |
Examples of repositioned drugs against trypanosomatid-caused diseases including the actual treatment, protein target and the new drug indication.
