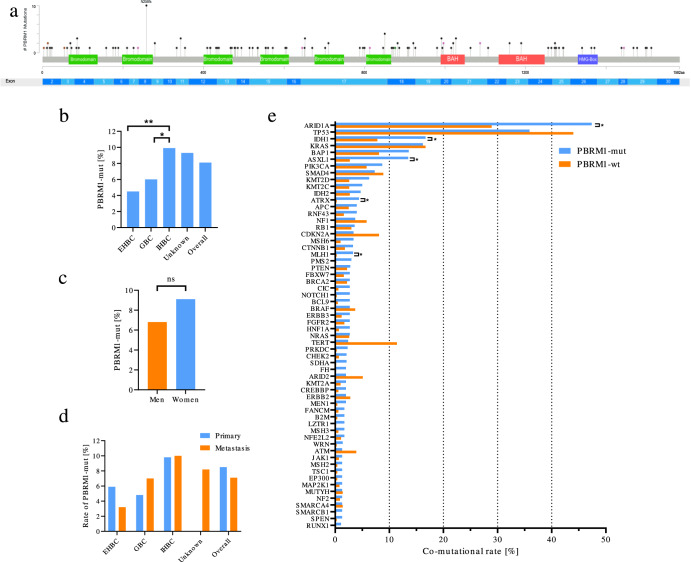
Fig. 1. Genomic context of PBRM1-mutated BTCs reveals high co-occurrence of mutations in chromatin remodeling genes.
a Lollipop plot showing the distribution of the detected PBRM1-mutations. The N258fs-mutation (Exon 8) was the most frequent pathogenic variant detected in our cohort. b Means of PBRM1 mutations according to anatomic location (extrahepatic biliary tract cancer (EHBC), gallbladder cancer (GBC), and intrahepatic biliary tract cancer (IHBC). Statistically significant differences by two-sided Man–Whitney U are indicated as *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. c Sex-specific rates of PBRM1 mutations. Chi-Square test not significant (ns). d Rates of PBRM1 mutations by anatomic location stratified by sampling location (Primary vs. Metastasis). e Bar plot showing the rate of co-mutations of the indicated genes in PBRM1-mut samples compared to PBRM1-wt samples. Statistically significant differences by two-sided Man–Whitney U test after correction for multiple testing using are indicated as *q < 0.05. f Bar plot showing the rate of co-mutation stratified by anatomic location. Stars indicate significance level (chi-square test). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01,***p < 0.001, all other not significant. IHBC intrahepatic biliary tract cancer, EHBC extrahepatic biliary tract cancer, GBC gallbladder cancer.