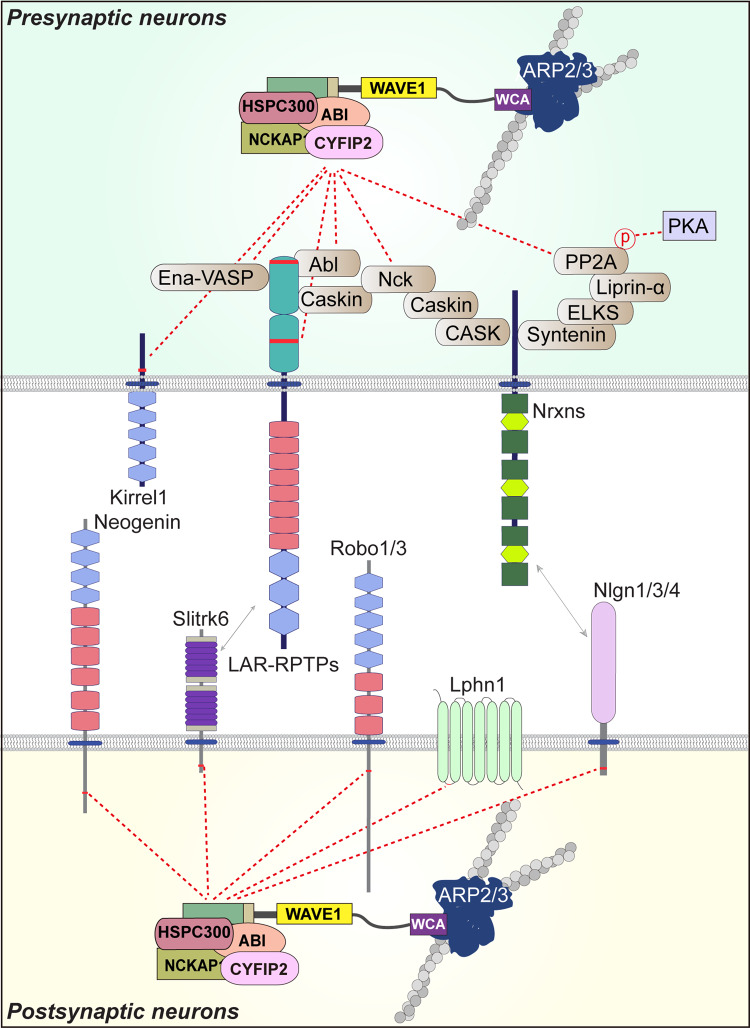
Fig. 2. Molecular model of WRC recruitment at neuronal synapses.
WRC recruitment is regulated by cell-adhesion proteins and their interacting scaffold proteins at synapses. Various scaffold proteins present in the presynaptic active zone play important roles in WRC recruitment and function. Prominent among them are LAR-RPTPs and Kirrel1. Neurexins (Nrxns) can also bind to the WRC but do not do so directly; instead, they bind indirectly through presynaptic scaffolding proteins, including syntenin, ELKS, liprin-α, PP2A, CASK, Caskins and Nck. In addition to interacting directly with the WRC through their WIRS motif, LAR-RPTPs can also indirectly bind the WRC through interactions with Ena, Abl, and Caskins. Robo receptors, Nlgns, neogenin, Slitrks, and latrophilins are also located at the postsynapse and might recruit the WRC through their WIRS motif.