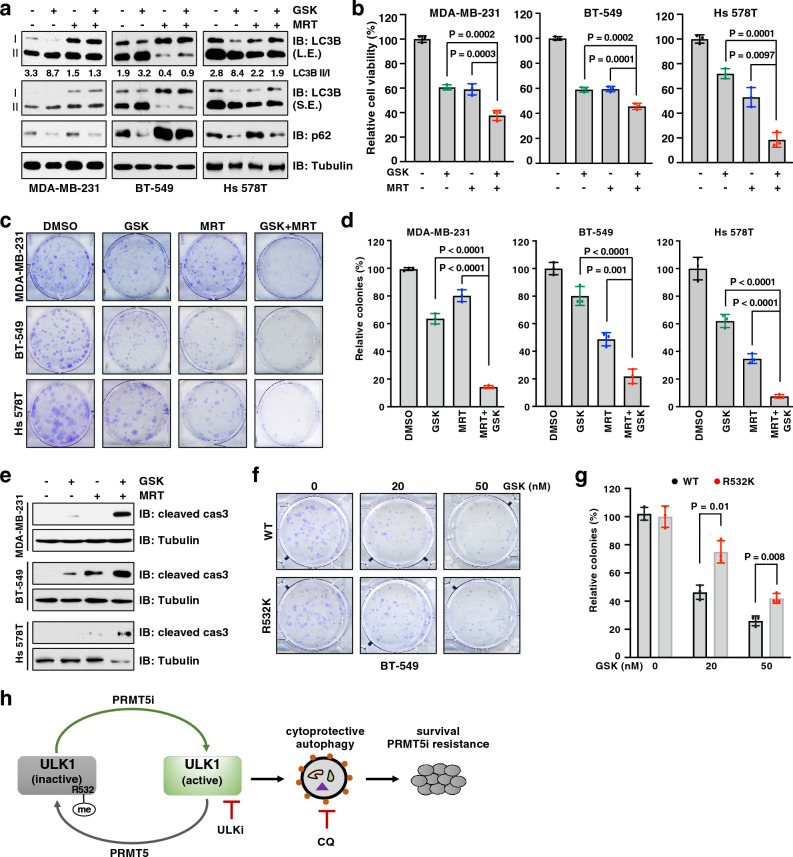
Figure 6.
ULK1 inhibitor enhances cellular sensitivity to PRMT5 inhibitor. (a) IB analysis of WCL derived from indicated cells treated with 1 μM GSK3326595 (GSK) and 300 nM, 1.5 μM, and 0.5 μM MRT68921 (MRT, ULK inhibitor) for MDA-MB-231, BT-549, and Hs 578T respectively for 3 days before harvesting. (b) Cell viability of MDA-MB-231, BT-549, and Hs 578T cells after treatment with 1 μM GSK and 300 nM, 1.5 μM, and 0.5 μM MRT, respectively, for 4 days (MDA-MB-231 and BT-549) and 6 days (Hs 578T). (c, d) MDA-MB-231, BT-549 and Hs 578T cells were treated with DMSO,100 nM, 15 nM, and 50 nM GSK, respectively, and MRT concentration as described in (b). (e) IB analysis of WCL derived from indicated cells after treatment with 1 μM GSK and MRT as described in (b) for 3 days. (f, g) BT-549 cells were depleted of endogenous ULK1 and re-introduced inducible ULK1-WT or R532K. The resulting cells were treated with 0, 20, and 50 nM GSK and subjected to colony formation assays. (h) Graphical model to depict PRMT5 regulates autophagy by methylating ULK1 and targeting autophagy for overcoming resistance to PRMT5 inhibitor. PRMT5i, PRMT5 inhibitor; ULK1i, ULK1 inhibitor; CQ, chloroquine. In (b, d, g) data are shown as the mean ± SD of n = 3 independent experiments. P values were calculated by Student’s t test. Similar results were obtained in n = 3 independent experiments in (a, e).