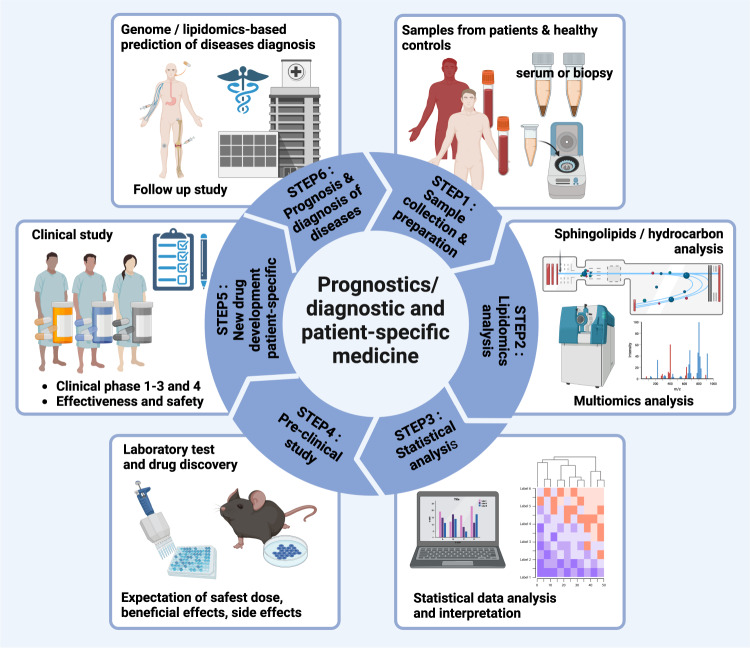
Fig. 3. Strategy for diagnosis/prognosis of diseases with sphingolipids.
Recent progress in metabolomics and multiomics analysis has enabled the investigation of sphingolipids as a marker of disease. After collection of human blood and disease tissue by biopsy, a series of procedures with mass spectrometry enable the detection of changes in sphingolipids and related molecules compared to levels in healthy volunteers. By analysis of a multiomics database, specific sphingolipids and related enzymes can be detected for human disease. Inhibition of sphingolipid enzymes in a preclinical disease model should enable investigation of the roles of sphingolipids and related enzymes.