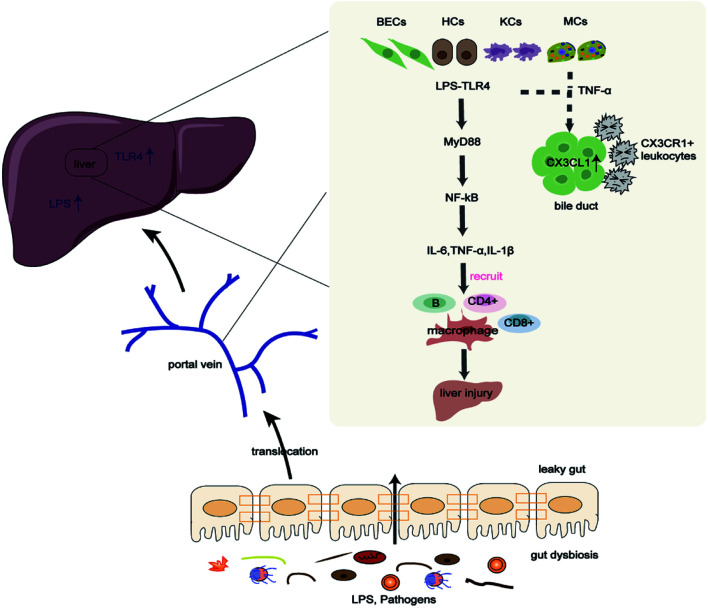
Fig. 1. Gut microbiota contributes to the pathogenesis of PBC through the LPS/TLR4 signaling pathway.
Gut dysbiosis and increased gut permeability promote pathogens and metabolite translocation to the liver, contributing to liver injury through the LPS/TLR4 signaling pathway. In addition, sensitized monocytes and TNF-α stimulate BECs to upregulate CX3CL1, causing cholangitis by interacting with CX3CR1+ leukocytes. BECs, bile duct epithelial cells; HCs, hepatocytes; IL, interleukin; KCs, Kupffer cells; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; MCs, monocytes; MyD88, myeloid differentiation factor 88; NF- κB, nuclear factor kappa-B; TLR4, Toll-like receptor 4; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-alpha.