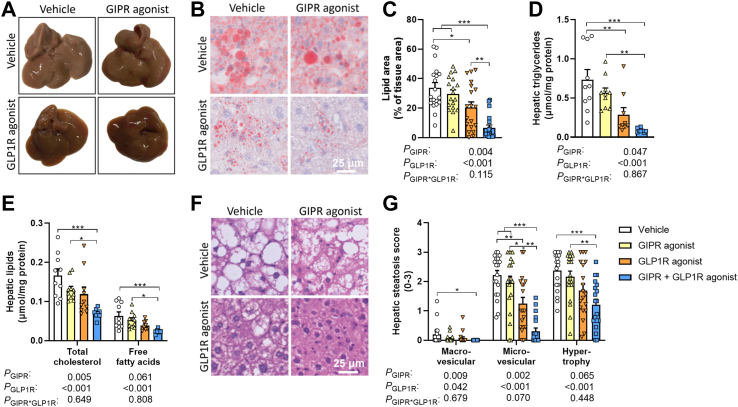
Fig. 3.
Combined GIPR/GLP1R agonism lowers hepatic steatosis. Male APOE∗3-Leiden.CETP mice were fed a high-fat high-cholesterol diet and received subcutaneous injections with either a GIPR agonist (GIPFA-085; 300 nmol/kg), a GLP1R agonist (GLP-140; 30 nmol/kg), both agonists at these doses, or vehicle every other day. After 10 weeks of treatment, (A) macroscopic pictures of representative livers were taken. (B–C) Cross-sections of the liver were stained with Oil red O to determine the hepatic lipid area. (D–E) Hepatic lipid content was assessed, and (F–G) NAFLD scores were determined on hematoxylin-eosin (H&E) stained cross-sections. Data are presented as mean ± SEM and individual data points. C, Gn = 18–19 per group; D–E, n = 8–10 per group. P values of two-way ANOVA are depicted below figure panels and symbols reflect statistical differences between groups as determined by Tukey post-hoc analysis with ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01 and ∗∗∗P < 0.001.