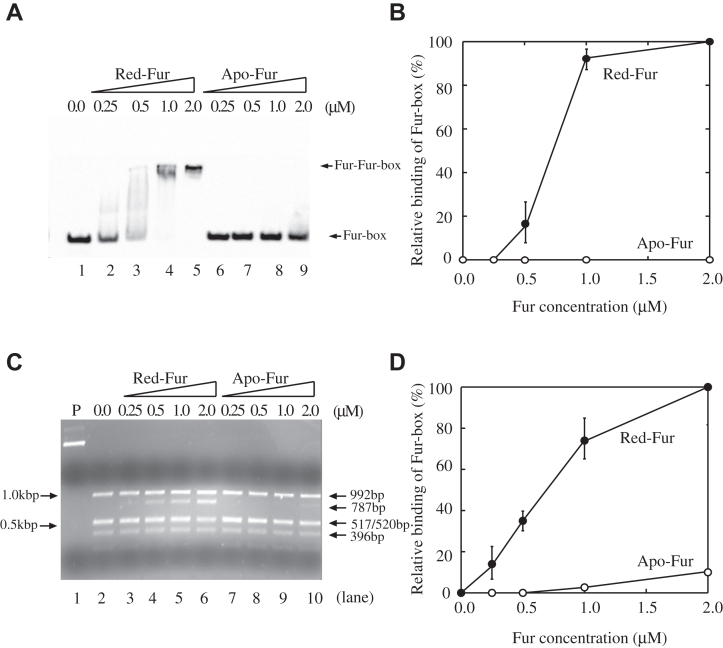
Figure 2.
The Fur-box binding activity of purified Red-Fur and Apo-Fur.A, band shift assays of Red-Fur and Apo-Fur. Biotin-labeled Fur-box DNA (0.7 nM) was incubated with the indicated concentrations of Red-Fur or Apo-Fur. Lane 1, no Fur protein. Lanes 2 to 5, biotin-labeled Fur-box DNA (0.7 nM) was incubated with 0.25 μM, 0.5 μM, 1.0 μM, and 2.0 μM Red-Fur, respectively. Lanes 6 to 9, biotin-labeled Fur-box DNA (0.7 nM) was incubated with 0.25 μM, 0.5 μM, 1.0 μM, and 2.0 μM Apo-Fur, respectively. B, relative binding activity of Red-Fur and Apo-Fur based on the band shift assays. The intensities of the Fur/Fur-box bands in shown (A) were quantified using ImageJ and plotted as a function of the Fur concentrations. Data represent the averages ± standard deviations from three independent experiments. C, the restriction site protection assays of Red-Fur and Apo-Fur. pUC18-iuc (3.2 nM) was preincubated with increasing concentrations of Red-Fur and Apo-Fur, followed by digestion with HinfI (1 unit) at 37 °C for 10 min. The digested DNA products were separated by 1.5% agarose gel electrophoresis. Lane 1, pUC18-iuc only. Lane 2, no Fur protein was added. Lanes 3 to 6, pUC18-iuc (3.2 nM) was preincubated with 0.25 μM, 0.5 μM, 1.0 μM, and 2.0 μM Red-Fur, respectively. Lanes 7 to 10, pUC18-iuc was preincubated with 0.25 μM, 0.5 μM, 1.0 μM, and 2.0 μM Apo-Fur, respectively. D, relative binding activity of Red-Fur and Apo-Fur based on the restriction site protection assays. The intensities of the DNA band at 787 bp shown in (C) were quantified using ImageJ and plotted as a function of the Fur concentrations. Data represent the averages ± standard deviations from three independent experiments.