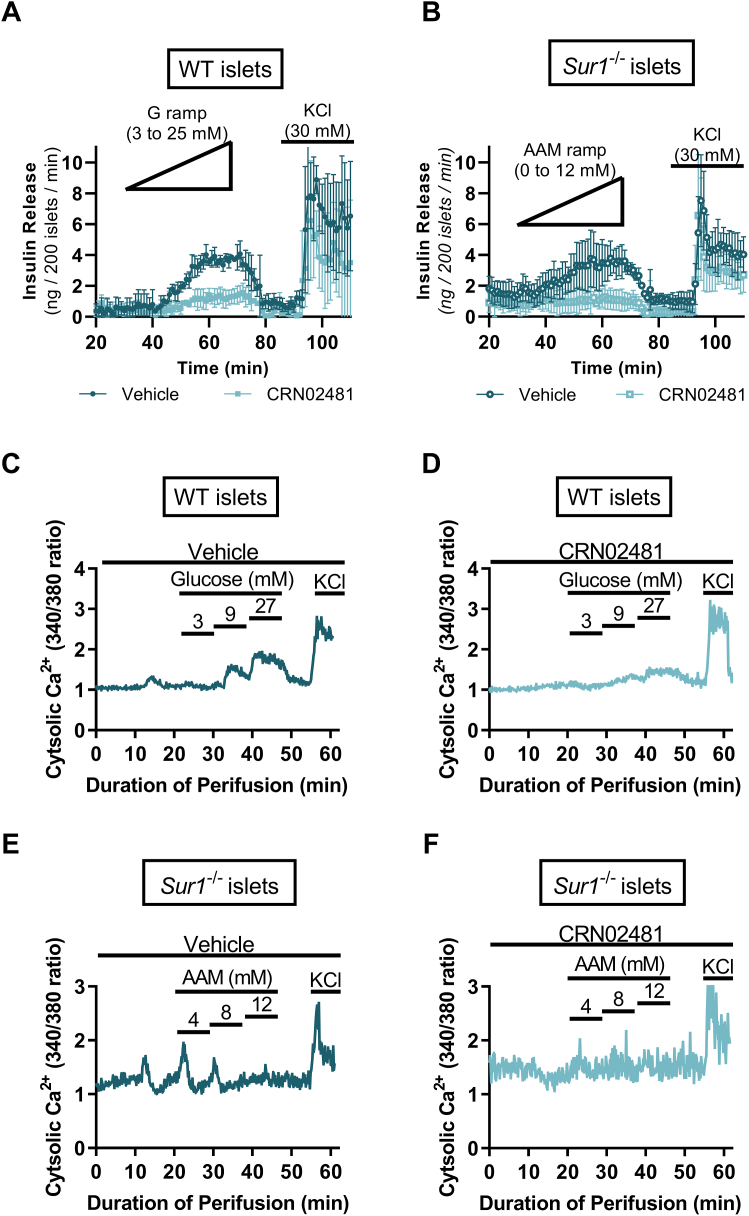
Figure 3.
CRN02481 significantly abrogates insulin secretion and calcium flux in response to glucose and amino acid stimulus. Perifusion of primary isolated islets to assess insulin release in (A) WT islets stimulated with glucose ramp (0–25 mM) and KCl (30 mM) or (B) Sur1−/− islets stimulated with amino acid (AA) ramp (0–12 mM) and KCl (30 mM). Two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons revealed that insulin release is significantly decreased with CRN02481 (500 nM) treatment for both WT (F(1, 384) = 94.75, p < 0.0001) and Sur1−/− (F(1,384) = 221.2, p < 0.0001) islets when compared to vehicle. (n = 3). Intracellular Ca2+ measurement of primary isolated islets for assessment of calcium signaling in WT islets treated with glucose steps (3 mM, 9 mM, 27 mM), KCl (30 mM), and (C) vehicle or (D) 500 nM CRN02481. Sur1−/− islets treated with amino acid steps (4 mM, 8 mM, and 12 mM), KCl (30 mM), and (E) vehicle or (F) 500 nM CRN02481. Two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons demonstrated that treatment with CRN02481 resulted in significantly decreased intracellular Ca2+ signaling in both WT (F(1, 3660) = 56.60, p < 0.0001) and Sur1−/− islets (F(1, 3660) = 799.0, p < 0.0001) compared to vehicle (n = 3–6). Data represent mean ± SD compared. WT, wild type.