Fig. 2.
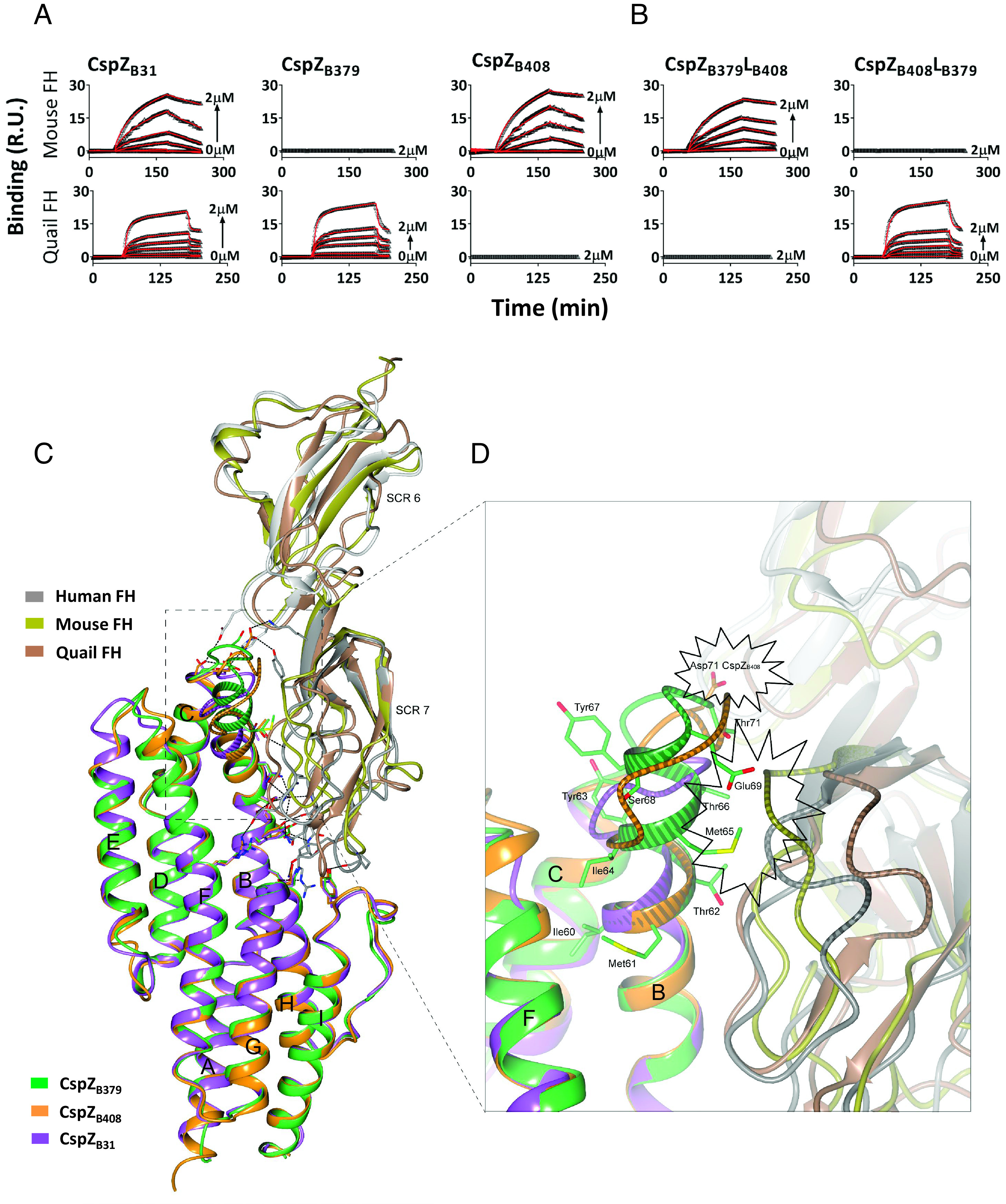
The polymorphic loop region in CspZ promotes host-specific FH-binding ability. (A and B) Untagged CspZ variants or mutants were flowed over the chip surface, conjugated with indicated FH variants. Binding was measured in response units (R.U.) by SPR. The kon, koff, and KD values were determined from the average of these three experiments (SI Appendix, Table S2). (C) The crystal structure of CspZB408-SCR6-7 where human SCR6-7 (gray) is superimposed with mouse SCR6-7 (gold, PDB: 2YBY), and the predicted structure of quail SCR6-7 (brown), while CspZB408 (orange) is superimposed with CspZB31 (purple) and CspZB379 (green). (D) The loop region in CspZ proteins located between α-helices B and C. The Asp71 in CspZB408, and the residues 60-IMTYIMTYSEGT-71 in CspZB379 are highlighted. The polymorphic loop region between α-helices B and C in CspZ variants, as well as the loop region in human, mouse and quail SCR6-7 located at the interface with helix-B in CspZ, is showed with a striped pattern. The potential structural hindrance region between CspZB408 and quail FH, as well as the structural hindrance between CspZB379 and both mouse and human FH, are indicated with the starbursts.
