Abstract
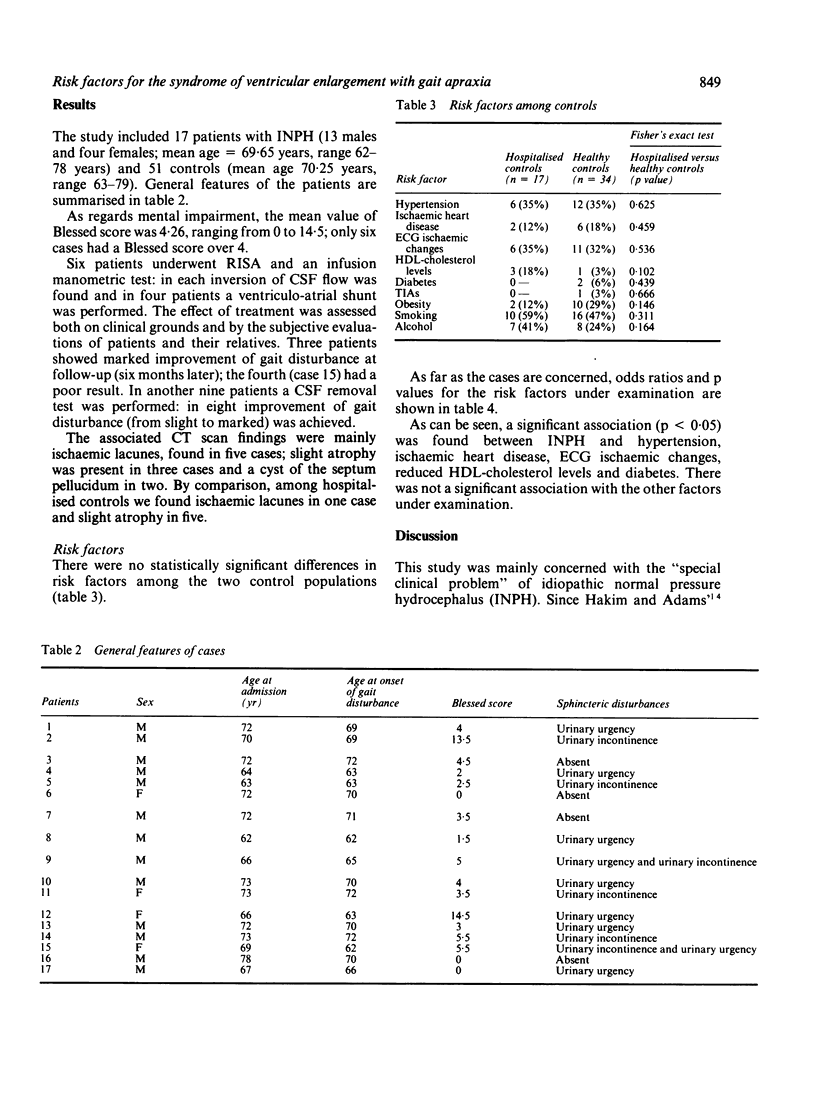
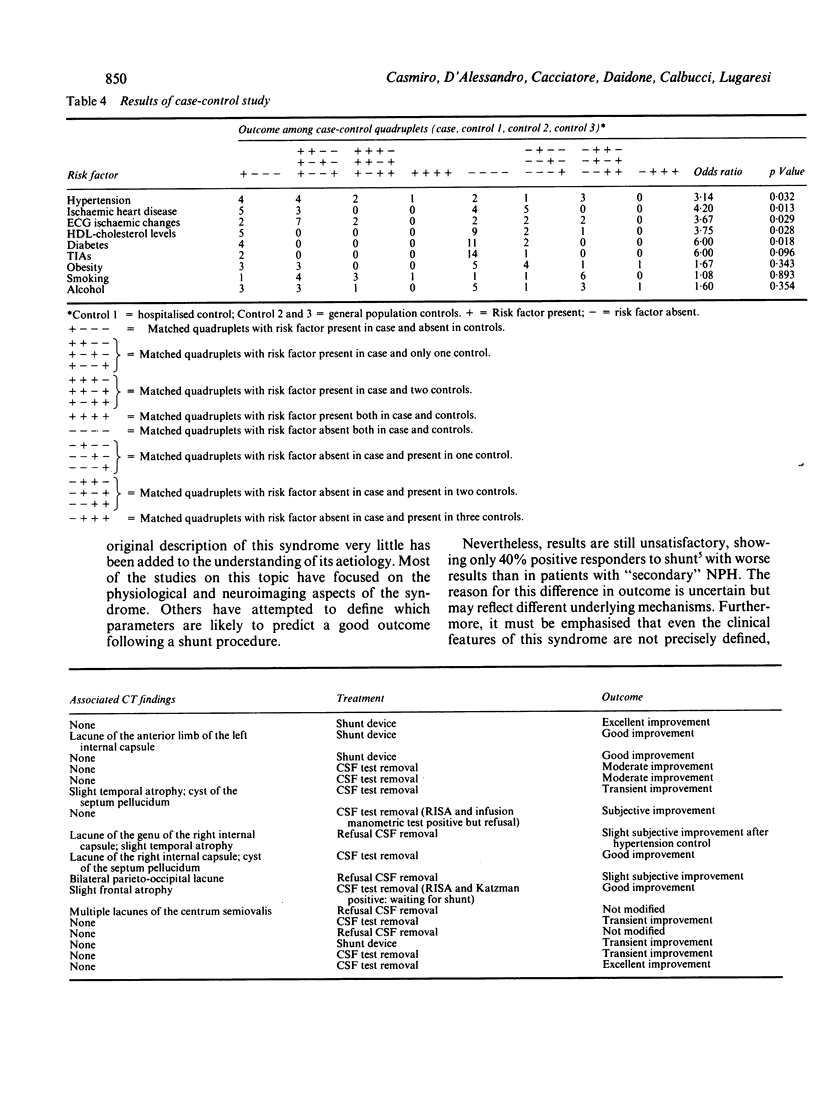
A case-control study was performed to verify the association between the risk factors for cerebrovascular disease and the syndrome of ventricular enlargement with gait apraxia (VEGAS). This syndrome was defined on the basis of clinical and CT criteria alone; however, it may be representative of patients with idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus in whom gait disturbance is the initial symptom. Seventeen patients were matched for age and sex with one hospitalised and two general population controls. Among the risk factors considered we found a significant statistical association between VEGAS and hypertension (odds ratio = 3.14; p = 0.032), ischaemic heart disease (odds ratio = 4.20; p = 0.013), ECG ischaemic changes (odds ratio = 3.67; p = 0.029), low HDL-cholesterol levels (odds ratio = 3.75; p = 0.028) and diabetes (odds ratio = 6.00; p = 0.018). Our findings indicate that risk factors for cerebrovascular disease may play a role in the development of VEGAS.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADAMS R. D., FISHER C. M., HAKIM S., OJEMANN R. G., SWEET W. H. SYMPTOMATIC OCCULT HYDROCEPHALUS WITH "NORMAL" CEREBROSPINAL-FLUID PRESSURE.A TREATABLE SYNDROME. N Engl J Med. 1965 Jul 15;273:117–126. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196507152730301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams R. D. Recent observations on normal pressure hydrocephalus. Schweiz Arch Neurol Neurochir Psychiatr. 1975;116(1):7–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blessed G., Tomlinson B. E., Roth M. The association between quantitative measures of dementia and of senile change in the cerebral grey matter of elderly subjects. Br J Psychiatry. 1968 Jul;114(512):797–811. doi: 10.1192/bjp.114.512.797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clough C. G. A case of normal pressure hydrocephalus presenting as levodopa responsive parkinsonism. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1987 Feb;50(2):234–234. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.50.2.234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DICHIRO G., REAMES P. M., MATTHEWS W. B., Jr RISA-VENTRICULOGRAPHY AND RISA-CISTERNOGRAPHY. Neurology. 1964 Mar;14:185–191. doi: 10.1212/wnl.14.3.185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLand F. H., James A. E., Jr, Ladd D. J., Konigsmark B. W. Normal pressure hydrocephalus: a histologic study. Am J Clin Pathol. 1972 Jul;58(1):58–63. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/58.1.58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earnest M. P., Fahn S., Karp J. H., Rowland L. P. Normal pressure hydrocephalus and hypertensive cerebrovascular disease. Arch Neurol. 1974 Oct;31(4):262–266. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1974.00490400076009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher C. M. Communicating hydrocephalus. Lancet. 1978 Jan 7;1(8054):37–37. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90378-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher C. M. Hydrocephalus as a cause of disturbances of gait in the elderly. Neurology. 1982 Dec;32(12):1358–1363. doi: 10.1212/wnl.32.12.1358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher C. M. The clinical picture in occult hydrocephalus. Clin Neurosurg. 1977;24:270–284. doi: 10.1093/neurosurgery/24.cn_suppl_1.270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graff-Radford N. R., Godersky J. C. Idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus and systemic hypertension. Neurology. 1987 May;37(5):868–871. doi: 10.1212/wnl.37.5.868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graff-Radford N. R., Godersky J. C. Normal-pressure hydrocephalus. Onset of gait abnormality before dementia predicts good surgical outcome. Arch Neurol. 1986 Sep;43(9):940–942. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1986.00520090068020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakim S., Adams R. D. The special clinical problem of symptomatic hydrocephalus with normal cerebrospinal fluid pressure. Observations on cerebrospinal fluid hydrodynamics. J Neurol Sci. 1965 Jul-Aug;2(4):307–327. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(65)90016-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzman R., Hussey F. A simple constant-infusion manometric test for measurement of CSF absorption. I. Rationale and method. Neurology. 1970 Jun;20(6):534–544. doi: 10.1212/wnl.20.6.534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzman R. Normal pressure hydrocephalus. Contemp Neurol Ser. 1977;15:69–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koto A., Rosenberg G., Zingesser L. H., Horoupian D., Katzman R. Syndrome of normal pressure hydrocephalus: possible relation to hypertensive and arteriosclerotic vasculopathy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1977 Jan;40(1):73–79. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.40.1.73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorenzo A. V., Bresnan M. J., Barlow C. F. Cerebrospinal fluid absorption deficit in normal pressure hydrocephalus. Arch Neurol. 1974 May;30(5):387–393. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1974.00490350045007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer J. S., Kitagawa Y., Tanahashi N., Tachibana H., Kandula P., Cech D. A., Clifton G. L., Rose J. E. Evaluation of treatment of normal-pressure hydrocephalus. J Neurosurg. 1985 Apr;62(4):513–521. doi: 10.3171/jns.1985.62.4.0513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shukla D., Singh B. M., Strobos R. J. Hypertensive cerebrovascular disease and normal pressure hydrocephalus. Neurology. 1980 Sep;30(9):998–1000. doi: 10.1212/wnl.30.9.998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sypert G. W., Leffman H., Ojemann G. A. Occult normal pressure hydrocephalus manifested by parkinsonism-dementia complex. Neurology. 1973 Mar;23(3):234–238. doi: 10.1212/wnl.23.3.234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassilouthis J. The syndrome of normal-pressure hydrocephalus. J Neurosurg. 1984 Sep;61(3):501–509. doi: 10.3171/jns.1984.61.3.0501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vessal K., Sperber E. E., James A. E., Jr Chronic communicating hydrocephalus with normal CSE pressures: a cisternographic-pathologic correlation. Ann Radiol (Paris) 1974 Dec;17(8):785–793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


