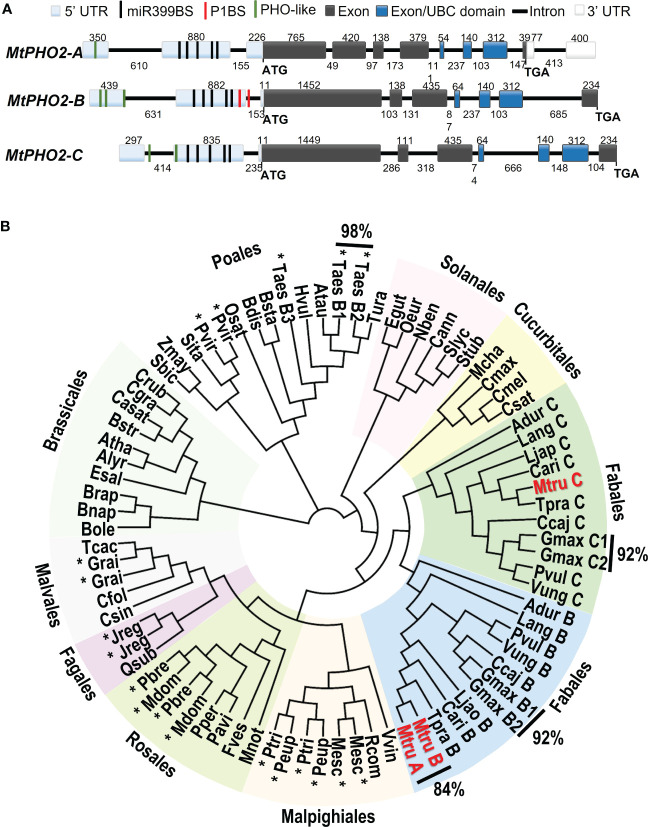
Figure 1.
Gene structure and phylogenetic relationships of Medicago truncatula PHO2-like genes. (A) Gene structure of the three PHO2 genes present in the A17 Medicago truncatula genome (Mt4.0v1) and validated using RNA-seq data. Only splicing variant MtPHO2-A.2 is shown here (see Supplementary Figure 1A for other slicing variants). Exons are shown as grey or darker blue boxes, with the latter encoding the ubiquitin-conjugating (UBC) domain (see also Supplementary Figure 1B ). UTRs are shaded light blue (5’ of the coding sequence) or white boxes (3’ of the coding sequence). The black, green and red lines depict the position within the 5’ UTR of the five potential miR399-binding sites (miR399BS), PHO-like elements, and the PHR1 binding sites (P1BS). Promoters and cis-regulatory motifs are detailed in Supplementary Figure 2 . Gene structures are drawn to scale, and the associated numbers indicate sizes (numbers above exons and below introns). (B) Phylogenetic tree of the PHO2-like gene family in plants. The different orders are marked next to different colored backgrounds. The Medicago truncatula PHO2 genes are indicated in red (MtruA, MtPHO2-A; MtruB, MtPHO2-B; MtruC, MtPHO2-C). The * indicates gene duplication events outside of the order Fabales. Values outside of the Phylogenetic tree show the percentages of homology between MtPHO2A and B proteins as well as some other plant species. The protein sequences were extracted from Phytozome and NCBI Protein databases. The circular phylogenetic tree was constructed from a ClustalW alignment of the full‐length protein sequences in Geneious software using Juker-Cantor as the genetic distance model and UPGMA as a tree build method with 500 replicates and 60% of support threshold. The gene IDs encoding each protein are described in Supplementary Table S1 .