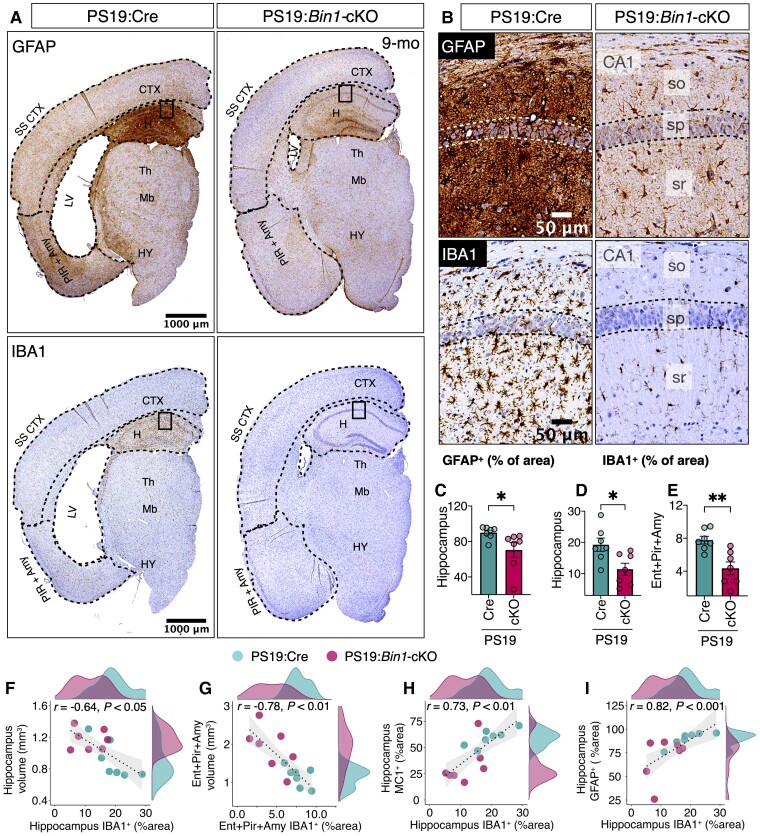
Figure 5.
Significant attenuation of neuroinflammation in the hippocampus of PS19:Bin1-cKO mice. (A) Representative images of GFAP and IBA1 immunostaining in hemibrains from 9-month-old mice. (B) Higher magnification of the hippocampus (boxed areas of images in A). (C–E) Quantification of GFAP or Iba1 expression in the hippocampus and Entorhinal/piriform/amygdala revealed significant decreases in PS19:Bin1-cKO (n = 7) mice compared to PS19:Cre (n = 7). (F–I) Spearman’s correlation coefficient analysis shows a negative correlation between IBA1 expression and the volumes of the hippocampus or Entorhinal/piriform/amygdala. Moreover, there is a positive correlation between hippocampal IBA1 expression and tau pathology or GFAP expression. PS19:Cre (n = 7) and PS19:Bin1-cKO (n = 7) mice. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01.