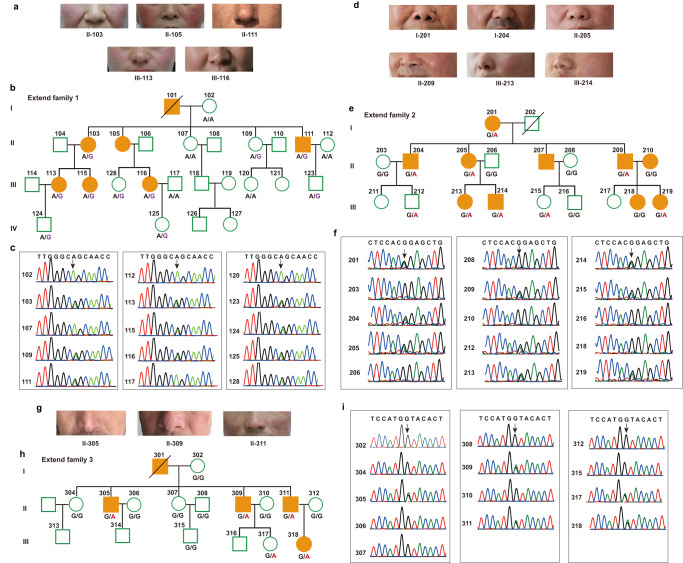
Fig. 2. Single rare deleterious variants are identified in large rosacea families.
a–c Images show the individuals with typical rosacea phenotypes in their central faces in large family 1 (a). Pedigree structure of the large family 1 (b). Solid symbols indicate individuals affected with rosacea; open symbols denote unaffected relatives; squares indicate male individuals; circles denote female individuals and slashes show deceased members. Chromatograms of Sanger sequencing show the heterozygous mutation in LRRC4 in large family 1 (c). d–f Images show the individuals affected with rosacea (d), pedigree structure (e), and Sanger sequencing chromatograms show the heterozygous mutation in SH3PXD2A (f) in large family 2. g–i Images show the individuals affected with rosacea (g), pedigree structure (h), and Sanger sequencing chromatograms show the heterozygous mutation in SLC26A8 (i) in large family 3.