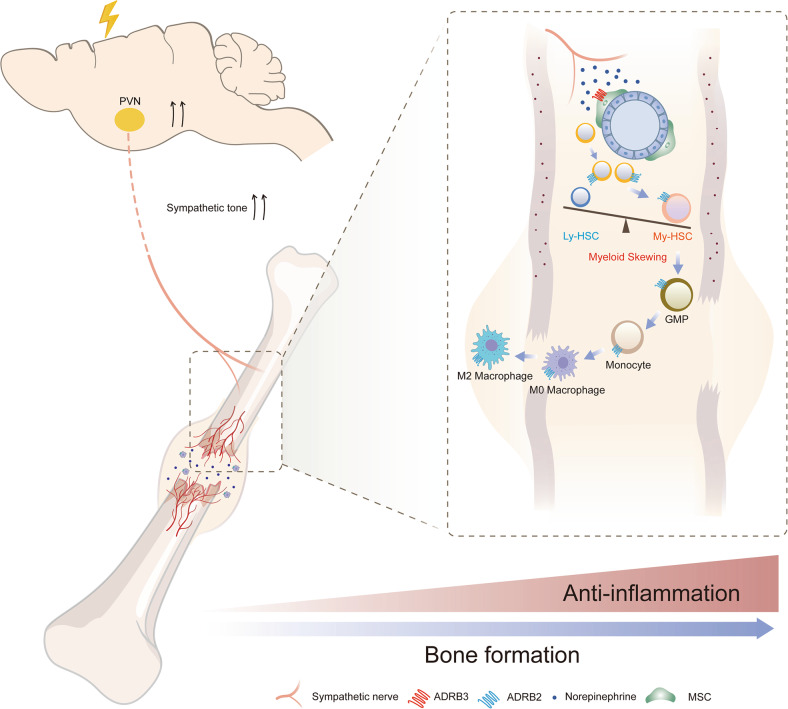
Fig. 9.
Graphic illustration of this study. Traumatic brain injury (TBI) activates hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus (PVN) to increase the sympathetic outflow. The elevated sympathetic tones trigger the proliferation of hematopoietic stem cells through β3-adrenergic receptor (ARs) in bone marrow. Importantly, the sympathetic hypersensitivity induced activation of β2-adrenergic signaling, which promotes myelopoiesis and M2 polarization of macrophages in callus. During the early stage of fracture healing, TBI-induced sympathetic hypersensitivity facilitates the anti-inflammation microenvironment in callus by activating β adrenergic receptors, therefore accelerates the fracture healing process. MSC mesenchymal stem cell, Ly-HSC lymphoid-biased hematopoietic stem cell, My-HSC myeloid-biased hematopoietic stem cell, GMP granulocyte monocyte progenitor