Abstract
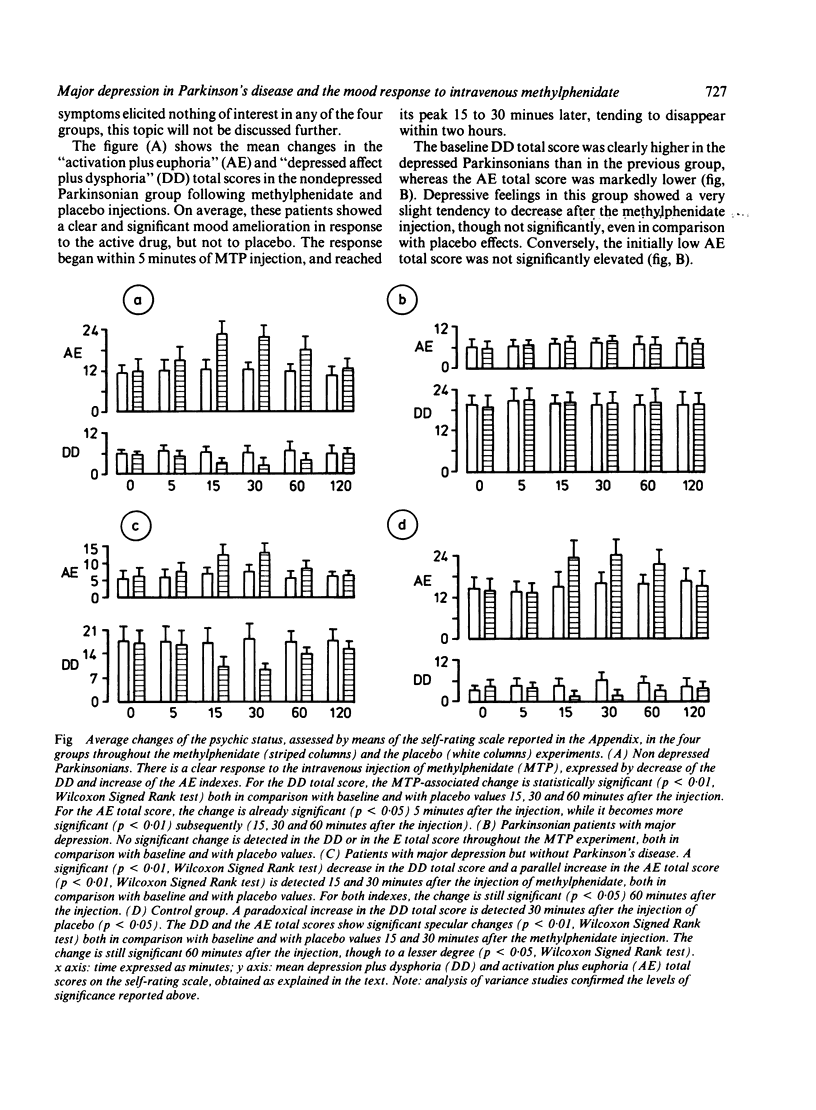
The euphoric response to equivalent doses of intravenous methylphenidate (MTP) was assessed in a group of 13 Parkinsonian patients affected by major depression, in a group of 11 nondepressed Parkinsonians, in a group of 14 nonparkinsonian subjects suffering from major depression, and finally in a group of 12 controls with no CNS or psychiatric disease. Subjects of all four groups were matched for age, sex and other main characteristics. Depressed and nondepressed Parkinsonians were also matched for duration and severity of illness, and for the type of antiparkinsonian treatment. The response to MTP was evaluated in the context of a double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Parkinsonian patients with major depression exhibited a significant lack of sensitivity to the euphoriant effects of MTP, in comparison with the other three groups. Euphoria produced by central stimulants has been shown to depend on the activity of a dopamine synapse in humans, which is thought to be situated at the limbic terminals of dopamine neurons located in the ventral tegmental area. Degeneration of this system may have predisposed our Parkinsonian patients to major depression.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashall F., Bramwell M. E., Harris H. A new marker for human cancer cells. 1 The Ca antigen and the Ca1 antibody. Lancet. 1982 Jul 3;2(8288):1–6. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)91150-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P., Brawley P. Dexamethasone suppression test and mood response to methylphenidate in primary depression. Am J Psychiatry. 1983 Aug;140(8):990–993. doi: 10.1176/ajp.140.8.990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantello R., Aguggia M., Gilli M., Delsedime M., Riccio A., Rainero I., Mutani R. Analgesic action of methylphenidate on parkinsonian sensory symptoms. Mechanisms and pathophysiological implications. Arch Neurol. 1988 Sep;45(9):973–976. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1988.00520330051010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantello R., Gilli M., Riccio A., Bergamasco B. Mood changes associated with "end-of-dose deterioration" in Parkinson's disease: a controlled study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1986 Oct;49(10):1182–1190. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.49.10.1182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantello R., Riccio A., Scarzella L., Leotta D., Bergamasco B. Depression in Parkinson disease: a disabling but neglected factor. Ital J Neurol Sci. 1984 Dec;5(4):417–422. doi: 10.1007/BF02042626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celesia G. G., Wanamaker W. M. Psychiatric disturbances in Parkinson's disease. Dis Nerv Syst. 1972 Sep;33(9):577–583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Direnfeld L. K., Albert M. L., Volicer L., Langlais P. J., Marquis J., Kaplan E. Parkinson's disease. The possible relationship of laterality to dementia and neurochemical findings. Arch Neurol. 1984 Sep;41(9):935–941. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1984.04050200041016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fawcett J., Clark D. C., Scheftner W. A., Gibbons R. D. Assessing anhedonia in psychiatric patients. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1983 Jan;40(1):79–84. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1983.01790010081010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fibiger H. C. The neurobiological substrates of depression in Parkinson's disease: a hypothesis. Can J Neurol Sci. 1984 Feb;11(1 Suppl):105–107. doi: 10.1017/s0317167100046230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folstein M. F., Folstein S. E., McHugh P. R. "Mini-mental state". A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res. 1975 Nov;12(3):189–198. doi: 10.1016/0022-3956(75)90026-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotham A. M., Brown R. G., Marsden C. D. 'Frontal' cognitive function in patients with Parkinson's disease 'on' and 'off' levodopa. Brain. 1988 Apr;111(Pt 2):299–321. doi: 10.1093/brain/111.2.299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotham A. M., Brown R. G., Marsden C. D. Depression in Parkinson's disease: a quantitative and qualitative analysis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1986 Apr;49(4):381–389. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.49.4.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALLIDAY A. M., NATHAN P. W. Methyl phenidate in parkinsonism. Br Med J. 1961 Jun 10;1(5240):1652–1655. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5240.1652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hachinski V. C., Iliff L. D., Zilhka E., Du Boulay G. H., McAllister V. L., Marshall J., Russell R. W., Symon L. Cerebral blood flow in dementia. Arch Neurol. 1975 Sep;32(9):632–637. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1975.00490510088009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn S. Some psychological factors in Parkinsonism. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1974 Jan;37(1):27–31. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.37.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Javoy-Agid F., Agid Y. Is the mesocortical dopaminergic system involved in Parkinson disease? Neurology. 1980 Dec;30(12):1326–1330. doi: 10.1212/wnl.30.12.1326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jönsson L. E., Anggård E., Gunne L. M. Blockade of intravenous amphetamine euphoria in man. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1971 Nov-Dec;12(6):889–896. doi: 10.1002/cpt1971126889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein D. F. Endogenomorphic depression. A conceptual and terminological revision. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1974 Oct;31(4):447–454. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1974.01760160005001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostić V. S., Djuricić B. M., Covicković-Sternić N., Bumbasirević L., Nikolić M., Mrsulja B. B. Depression and Parkinson's disease: possible role of serotonergic mechanisms. J Neurol. 1987 Feb;234(2):94–96. doi: 10.1007/BF00314109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyness W. H., Friedle N. M., Moore K. E. Destruction of dopaminergic nerve terminals in nucleus accumbens: effect on d-amphetamine self-administration. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1979 Nov;11(5):553–556. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(79)90040-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden C. D., Parkes J. D. "On-off" effects in patients with Parkinson's disease on chronic levodopa therapy. Lancet. 1976 Feb 7;1(7954):292–296. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)91416-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh G. G., Markham C. H. Does levodopa alter depression and psychopathology in Parkinsonism patients? J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1973 Dec;36(6):925–935. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.36.6.925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W. R., Sloan J. W., Sapira J. D., Jasinski D. R. Physiologic, subjective, and behavioral effects of amphetamine, methamphetamine, ephedrine, phenmetrazine, and methylphenidate in man. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1971 Mar-Apr;12(2):245–258. doi: 10.1002/cpt1971122part1245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayeux R., Stern Y., Cote L., Williams J. B. Altered serotonin metabolism in depressed patients with parkinson's disease. Neurology. 1984 May;34(5):642–646. doi: 10.1212/wnl.34.5.642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayeux R., Stern Y., Rosen J., Leventhal J. Depression, intellectual impairment, and Parkinson disease. Neurology. 1981 Jun;31(6):645–650. doi: 10.1212/wnl.31.6.645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meehl P. E. Hedonic capacity: some conjectures. Bull Menninger Clin. 1975 Jul;39(4):295–307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nauta W. J., Domesick V. B. Afferent and efferent relationships of the basal ganglia. Ciba Found Symp. 1984;107:3–29. doi: 10.1002/9780470720882.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelps M. E., Mazziotta J. C., Baxter L., Gerner R. Positron emission tomographic study of affective disorders: problems and strategies. Ann Neurol. 1984;15 (Suppl):S149–S156. doi: 10.1002/ana.410150729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips A. G., Fibiger H. C. The role of dopamine in maintaining intracranial self-stimulation in the ventral tegmentum, nucleus accumbens, and medial prefrontal cortex. Can J Psychol. 1978 Jun;32(2):58–66. doi: 10.1037/h0081676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins A. H. Depression in patients with Parkinsonism. Br J Psychiatry. 1976 Feb;128:141–145. doi: 10.1192/bjp.128.2.141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santamaría J., Tolosa E., Valles A. Parkinson's disease with depression: a possible subgroup of idiopathic parkinsonism. Neurology. 1986 Aug;36(8):1130–1133. doi: 10.1212/wnl.36.8.1130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern Y., Mayeux R., Rosen J. Contribution of perceptual motor dysfunction to construction and tracing disturbances in Parkinson's disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1984 Sep;47(9):983–989. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.47.9.983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor A. E., Saint-Cyr J. A., Lang A. E., Kenny F. T. Parkinson's disease and depression. A critical re-evaluation. Brain. 1986 Apr;109(Pt 2):279–292. doi: 10.1093/brain/109.2.279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhl G. R., Hedreen J. C., Price D. L. Parkinson's disease: loss of neurons from the ventral tegmental area contralateral to therapeutic surgical lesions. Neurology. 1985 Aug;35(8):1215–1218. doi: 10.1212/wnl.35.8.1215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Kammen D. P., Murphy D. L. Attenuation of the euphoriant and activating effects of d- and l-amphetamine by lithium carbonate treatment. Psychopharmacologia. 1975 Nov 21;44(3):215–224. doi: 10.1007/BF00428897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wald D., Ebstein R. P., Belmaker R. H. Haloperidol and lithium blocking of the mood response to intravenous methylphenidate. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1978 Apr 14;57(1):83–87. doi: 10.1007/BF00426962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warburton J. W. Depressive symptoms in Parkinson patients referred for thalamotomy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1967 Aug;30(4):368–370. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.30.4.368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


