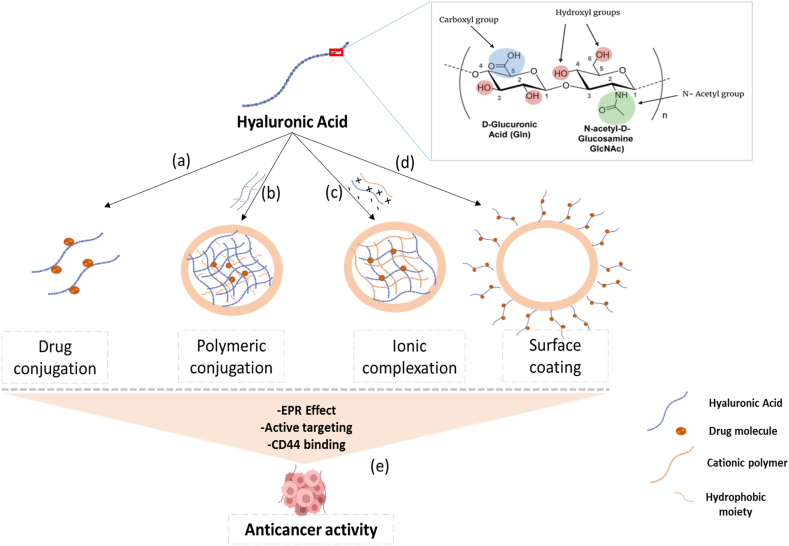
Fig. 3.
The application of hyaluronic acid-based nanocarriers in cancer treatment. (a) and (b) Direct conjugation of cytotoxic drug with HA or hydrophobic moiety results in self-assembly of nanoparticles (NPs) that can be administered intravenously for cancer cell targeting; (b) HA hydrogel formation using a cationic polymer; (c) Surface coating of NP with HA; (e) Hyaluronic acid-based drug nanocarriers permeate cancerous tissues via EPR effect and binds to the CD44 receptor site to elicit anticancer activity.